Page 380 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 380
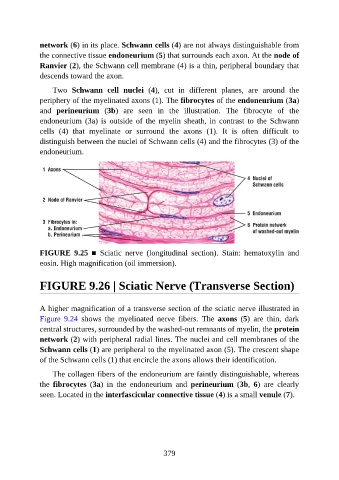
network (6) in its place. Schwann cells (4) are not always distinguishable from
the connective tissue endoneurium (5) that surrounds each axon. At the node of
Ranvier (2), the Schwann cell membrane (4) is a thin, peripheral boundary that
descends toward the axon.
Two Schwann cell nuclei (4), cut in different planes, are around the
periphery of the myelinated axons (1). The fibrocytes of the endoneurium (3a)
and perineurium (3b) are seen in the illustration. The fibrocyte of the
endoneurium (3a) is outside of the myelin sheath, in contrast to the Schwann
cells (4) that myelinate or surround the axons (1). It is often difficult to
distinguish between the nuclei of Schwann cells (4) and the fibrocytes (3) of the
endoneurium.
FIGURE 9.25 ■ Sciatic nerve (longitudinal section). Stain: hematoxylin and
eosin. High magnification (oil immersion).
FIGURE 9.26 | Sciatic Nerve (Transverse Section)
A higher magnification of a transverse section of the sciatic nerve illustrated in
Figure 9.24 shows the myelinated nerve fibers. The axons (5) are thin, dark
central structures, surrounded by the washed-out remnants of myelin, the protein
network (2) with peripheral radial lines. The nuclei and cell membranes of the
Schwann cells (1) are peripheral to the myelinated axon (5). The crescent shape
of the Schwann cells (1) that encircle the axons allows their identification.
The collagen fibers of the endoneurium are faintly distinguishable, whereas
the fibrocytes (3a) in the endoneurium and perineurium (3b, 6) are clearly
seen. Located in the interfascicular connective tissue (4) is a small venule (7).
379