Page 661 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 661
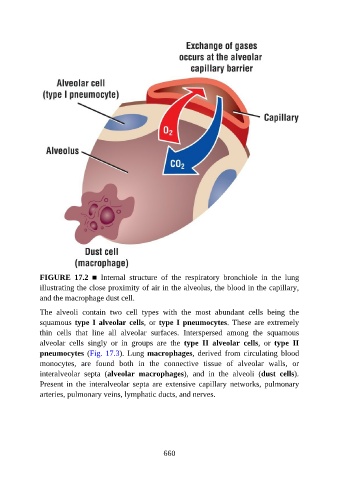
FIGURE 17.2 ■ Internal structure of the respiratory bronchiole in the lung
illustrating the close proximity of air in the alveolus, the blood in the capillary,
and the macrophage dust cell.
The alveoli contain two cell types with the most abundant cells being the
squamous type I alveolar cells, or type I pneumocytes. These are extremely
thin cells that line all alveolar surfaces. Interspersed among the squamous
alveolar cells singly or in groups are the type II alveolar cells, or type II
pneumocytes (Fig. 17.3). Lung macrophages, derived from circulating blood
monocytes, are found both in the connective tissue of alveolar walls, or
interalveolar septa (alveolar macrophages), and in the alveoli (dust cells).
Present in the interalveolar septa are extensive capillary networks, pulmonary
arteries, pulmonary veins, lymphatic ducts, and nerves.
660