Page 723 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 723
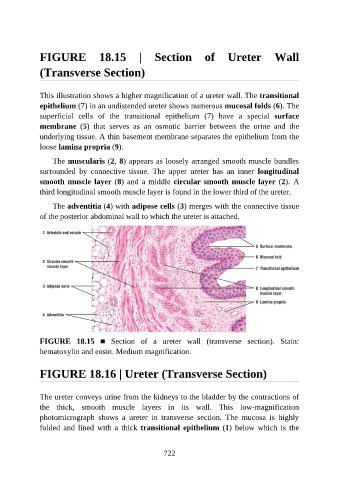
FIGURE 18.15 | Section of Ureter Wall
(Transverse Section)
This illustration shows a higher magnification of a ureter wall. The transitional
epithelium (7) in an undistended ureter shows numerous mucosal folds (6). The
superficial cells of the transitional epithelium (7) have a special surface
membrane (5) that serves as an osmotic barrier between the urine and the
underlying tissue. A thin basement membrane separates the epithelium from the
loose lamina propria (9).
The muscularis (2, 8) appears as loosely arranged smooth muscle bundles
surrounded by connective tissue. The upper ureter has an inner longitudinal
smooth muscle layer (8) and a middle circular smooth muscle layer (2). A
third longitudinal smooth muscle layer is found in the lower third of the ureter.
The adventitia (4) with adipose cells (3) merges with the connective tissue
of the posterior abdominal wall to which the ureter is attached.
FIGURE 18.15 ■ Section of a ureter wall (transverse section). Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. Medium magnification.
FIGURE 18.16 | Ureter (Transverse Section)
The ureter conveys urine from the kidneys to the bladder by the contractions of
the thick, smooth muscle layers in its wall. This low-magnification
photomicrograph shows a ureter in transverse section. The mucosa is highly
folded and lined with a thick transitional epithelium (1) below which is the
722