Page 725 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 725
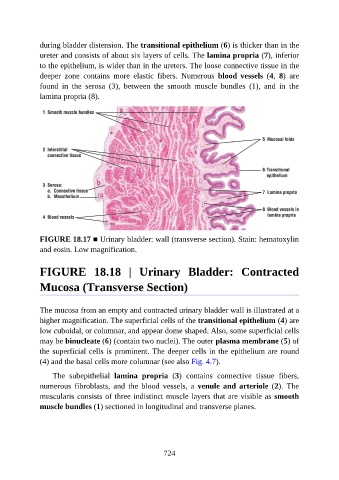
during bladder distension. The transitional epithelium (6) is thicker than in the
ureter and consists of about six layers of cells. The lamina propria (7), inferior
to the epithelium, is wider than in the ureters. The loose connective tissue in the
deeper zone contains more elastic fibers. Numerous blood vessels (4, 8) are
found in the serosa (3), between the smooth muscle bundles (1), and in the
lamina propria (8).
FIGURE 18.17 ■ Urinary bladder: wall (transverse section). Stain: hematoxylin
and eosin. Low magnification.
FIGURE 18.18 | Urinary Bladder: Contracted
Mucosa (Transverse Section)
The mucosa from an empty and contracted urinary bladder wall is illustrated at a
higher magnification. The superficial cells of the transitional epithelium (4) are
low cuboidal, or columnar, and appear dome shaped. Also, some superficial cells
may be binucleate (6) (contain two nuclei). The outer plasma membrane (5) of
the superficial cells is prominent. The deeper cells in the epithelium are round
(4) and the basal cells more columnar (see also Fig. 4.7).
The subepithelial lamina propria (3) contains connective tissue fibers,
numerous fibroblasts, and the blood vessels, a venule and arteriole (2). The
muscularis consists of three indistinct muscle layers that are visible as smooth
muscle bundles (1) sectioned in longitudinal and transverse planes.
724