Page 752 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 752
FIGURE 19.5 ■ Cell types in the hypophysis. Stain: modified Azan. Oil
immersion.
FIGURE 19.6 | Hypophysis: Pars Distalis, Pars
Intermedia, and Pars Nervosa
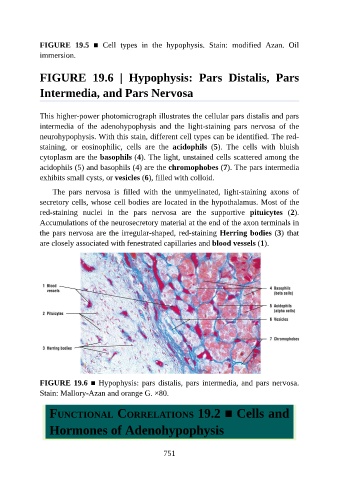
This higher-power photomicrograph illustrates the cellular pars distalis and pars
intermedia of the adenohypophysis and the light-staining pars nervosa of the
neurohypophysis. With this stain, different cell types can be identified. The red-
staining, or eosinophilic, cells are the acidophils (5). The cells with bluish
cytoplasm are the basophils (4). The light, unstained cells scattered among the
acidophils (5) and basophils (4) are the chromophobes (7). The pars intermedia
exhibits small cysts, or vesicles (6), filled with colloid.
The pars nervosa is filled with the unmyelinated, light-staining axons of
secretory cells, whose cell bodies are located in the hypothalamus. Most of the
red-staining nuclei in the pars nervosa are the supportive pituicytes (2).
Accumulations of the neurosecretory material at the end of the axon terminals in
the pars nervosa are the irregular-shaped, red-staining Herring bodies (3) that
are closely associated with fenestrated capillaries and blood vessels (1).
FIGURE 19.6 ■ Hypophysis: pars distalis, pars intermedia, and pars nervosa.
Stain: Mallory-Azan and orange G. ×80.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 19.2 ■ Cells and
Hormones of Adenohypophysis
751