Page 776 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 776
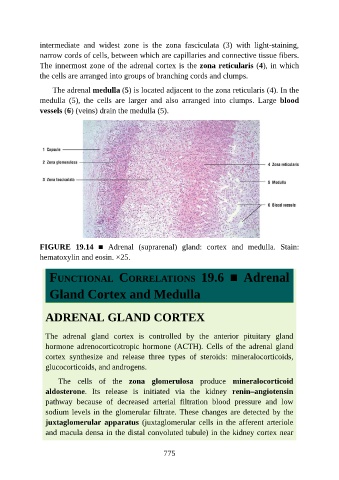
intermediate and widest zone is the zona fasciculata (3) with light-staining,
narrow cords of cells, between which are capillaries and connective tissue fibers.
The innermost zone of the adrenal cortex is the zona reticularis (4), in which
the cells are arranged into groups of branching cords and clumps.
The adrenal medulla (5) is located adjacent to the zona reticularis (4). In the
medulla (5), the cells are larger and also arranged into clumps. Large blood
vessels (6) (veins) drain the medulla (5).
FIGURE 19.14 ■ Adrenal (suprarenal) gland: cortex and medulla. Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. ×25.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 19.6 ■ Adrenal
Gland Cortex and Medulla
ADRENAL GLAND CORTEX
The adrenal gland cortex is controlled by the anterior pituitary gland
hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Cells of the adrenal gland
cortex synthesize and release three types of steroids: mineralocorticoids,
glucocorticoids, and androgens.
The cells of the zona glomerulosa produce mineralocorticoid
aldosterone. Its release is initiated via the kidney renin–angiotensin
pathway because of decreased arterial filtration blood pressure and low
sodium levels in the glomerular filtrate. These changes are detected by the
juxtaglomerular apparatus (juxtaglomerular cells in the afferent arteriole
and macula densa in the distal convoluted tubule) in the kidney cortex near
775