Page 901 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 901
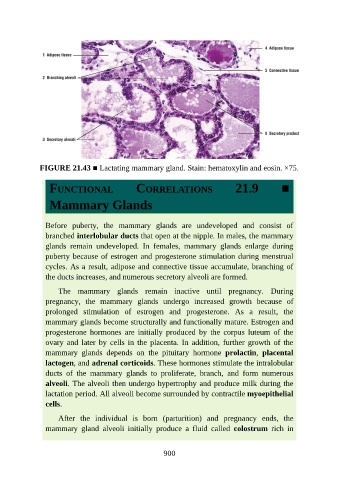
FIGURE 21.43 ■ Lactating mammary gland. Stain: hematoxylin and eosin. ×75.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 21.9 ■
Mammary Glands
Before puberty, the mammary glands are undeveloped and consist of
branched interlobular ducts that open at the nipple. In males, the mammary
glands remain undeveloped. In females, mammary glands enlarge during
puberty because of estrogen and progesterone stimulation during menstrual
cycles. As a result, adipose and connective tissue accumulate, branching of
the ducts increases, and numerous secretory alveoli are formed.
The mammary glands remain inactive until pregnancy. During
pregnancy, the mammary glands undergo increased growth because of
prolonged stimulation of estrogen and progesterone. As a result, the
mammary glands become structurally and functionally mature. Estrogen and
progesterone hormones are initially produced by the corpus luteum of the
ovary and later by cells in the placenta. In addition, further growth of the
mammary glands depends on the pituitary hormone prolactin, placental
lactogen, and adrenal corticoids. These hormones stimulate the intralobular
ducts of the mammary glands to proliferate, branch, and form numerous
alveoli. The alveoli then undergo hypertrophy and produce milk during the
lactation period. All alveoli become surrounded by contractile myoepithelial
cells.
After the individual is born (parturition) and pregnancy ends, the
mammary gland alveoli initially produce a fluid called colostrum rich in
900