Page 944 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 944
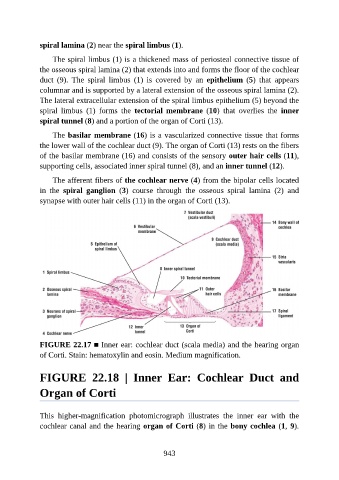
spiral lamina (2) near the spiral limbus (1).
The spiral limbus (1) is a thickened mass of periosteal connective tissue of
the osseous spiral lamina (2) that extends into and forms the floor of the cochlear
duct (9). The spiral limbus (1) is covered by an epithelium (5) that appears
columnar and is supported by a lateral extension of the osseous spiral lamina (2).
The lateral extracellular extension of the spiral limbus epithelium (5) beyond the
spiral limbus (1) forms the tectorial membrane (10) that overlies the inner
spiral tunnel (8) and a portion of the organ of Corti (13).
The basilar membrane (16) is a vascularized connective tissue that forms
the lower wall of the cochlear duct (9). The organ of Corti (13) rests on the fibers
of the basilar membrane (16) and consists of the sensory outer hair cells (11),
supporting cells, associated inner spiral tunnel (8), and an inner tunnel (12).
The afferent fibers of the cochlear nerve (4) from the bipolar cells located
in the spiral ganglion (3) course through the osseous spiral lamina (2) and
synapse with outer hair cells (11) in the organ of Corti (13).
FIGURE 22.17 ■ Inner ear: cochlear duct (scala media) and the hearing organ
of Corti. Stain: hematoxylin and eosin. Medium magnification.
FIGURE 22.18 | Inner Ear: Cochlear Duct and
Organ of Corti
This higher-magnification photomicrograph illustrates the inner ear with the
cochlear canal and the hearing organ of Corti (8) in the bony cochlea (1, 9).
943