Page 943 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 943
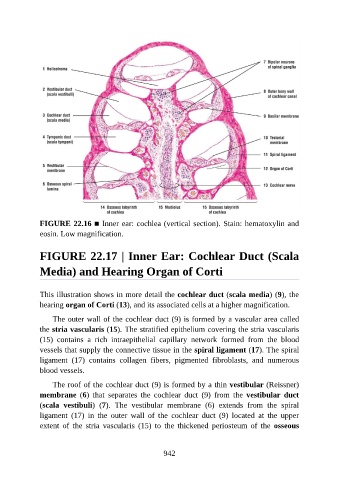
FIGURE 22.16 ■ Inner ear: cochlea (vertical section). Stain: hematoxylin and
eosin. Low magnification.
FIGURE 22.17 | Inner Ear: Cochlear Duct (Scala
Media) and Hearing Organ of Corti
This illustration shows in more detail the cochlear duct (scala media) (9), the
hearing organ of Corti (13), and its associated cells at a higher magnification.
The outer wall of the cochlear duct (9) is formed by a vascular area called
the stria vascularis (15). The stratified epithelium covering the stria vascularis
(15) contains a rich intraepithelial capillary network formed from the blood
vessels that supply the connective tissue in the spiral ligament (17). The spiral
ligament (17) contains collagen fibers, pigmented fibroblasts, and numerous
blood vessels.
The roof of the cochlear duct (9) is formed by a thin vestibular (Reissner)
membrane (6) that separates the cochlear duct (9) from the vestibular duct
(scala vestibuli) (7). The vestibular membrane (6) extends from the spiral
ligament (17) in the outer wall of the cochlear duct (9) located at the upper
extent of the stria vascularis (15) to the thickened periosteum of the osseous
942