Page 6 - Critical Control flipbook_Neat
P. 6
B Determine
Critical Controls
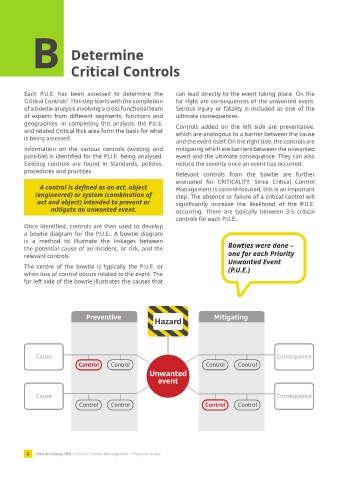
Each P.U.E. has been assessed to determine the can lead directly to the event taking place. On the
‘Critical Controls’. This step starts with the completion far right are consequences of the unwanted event.
of a bowtie analysis involving a cross functional team Serious injury or fatality is included as one of the
of experts from different segments, functions and ultimate consequences.
geographies. In completing this analysis, the P.U.E. Controls added on the left side are preventative,
and related Critical Risk area form the basis for what which are analogous to a barrier between the cause
is being assessed.
and the event itself. On the right side, the controls are
Information on the various controls (existing and mitigating which are barriers between the unwanted
possible) is identified for the P.U.E. being analysed. event and the ultimate consequence. They can also
Existing controls are found in Standards, policies, reduce the severity once an event has occurred.
procedures and practices. Relevant controls from the bowtie are further
evaluated for CRITICALITY. Since Critical Control
A control is defined as an act, object Management is control-focused, this is an important
(engineered) or system (combination of step. The absence or failure of a critical control will
act and object) intended to prevent or significantly increase the likelihood of the P.U.E.
mitigate an unwanted event. occurring. There are typically between 3-5 critical
controls for each P.U.E..
Once identified, controls are then used to develop
a bowtie diagram for the P.U.E.. A bowtie diagram
is a method to illustrate the linkages between
the potential cause of an incident, or risk, and the Bowties were done –
relevant controls. one for each Priority
Unwanted Event
The centre of the bowtie is typically the P.U.E. or (P.U.E.)
when loss of control occurs related to the event. The
far left side of the bowtie illustrates the causes that
Preventive Mitigating
Hazard
Cause Consequence
Control Control Control Control
Unwanted
event
Cause Consequence
Control Control Control Control
6 Holcim Group HSE • Critical Control Management - Program Guide