Page 243 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 243
MICROCONTROLLERS 229
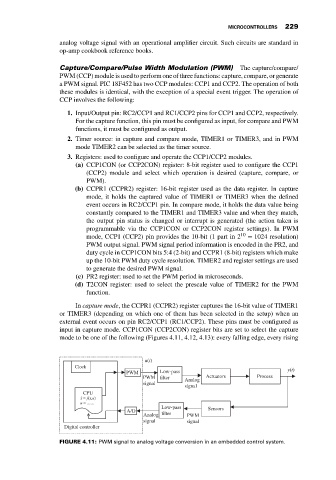
analog voltage signal with an operational amplifier circuit. Such circuits are standard in
op-amp cookbook reference books.
Capture/Compare/Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) The capture/compare/
PWM (CCP) module is used to perform one of three functions: capture, compare, or generate
a PWM signal. PIC 18F452 has two CCP modules: CCP1 and CCP2. The operation of both
these modules is identical, with the exception of a special event trigger. The operation of
CCP involves the following:
1. Input/Output pin: RC2/CCP1 and RC1/CCP2 pins for CCP1 and CCP2, respectively.
For the capture function, this pin must be configured as input, for compare and PWM
functions, it must be configured as output.
2. Timer source: in capture and compare mode, TIMER1 or TIMER3, and in PWM
mode TIMER2 can be selected as the timer source.
3. Registers: used to configure and operate the CCP1/CCP2 modules.
(a) CCP1CON (or CCP2CON) register: 8-bit register used to configure the CCP1
(CCP2) module and select which operation is desired (capture, compare, or
PWM).
(b) CCPR1 (CCPR2) register: 16-bit register used as the data register. In capture
mode, it holds the captured value of TIMER1 or TIMER3 when the defined
event occurs in RC2/CCP1 pin. In compare mode, it holds the data value being
constantly compared to the TIMER1 and TIMER3 value and when they match,
the output pin status is changed or interrupt is generated (the action taken is
programmable via the CCP1CON or CCP2CON register settings). In PWM
mode, CCP1 (CCP2) pin provides the 10-bit (1 part in 2 10 = 1024 resolution)
PWM output signal. PWM signal period information is encoded in the PR2, and
duty cycle in CCP1CON bits 5:4 (2-bit) and CCPR1 (8-bit) registers which make
up the 10-bit PWM duty cycle resolution. TIMER2 and register settings are used
to generate the desired PWM signal.
(c) PR2 register: used to set the PWM period in microseconds.
(d) T2CON register: used to select the prescale value of TIMER2 for the PWM
function.
In capture mode, the CCPR1 (CCPR2) register captures the 16-bit value of TIMER1
or TIMER3 (depending on which one of them has been selected in the setup) when an
external event occurs on pin RC2/CCP1 (RC1/CCP2). These pins must be configured as
input in capture mode. CCP1CON (CCP2CON) register bits are set to select the capture
mode to be one of the following (Figures 4.11, 4.12, 4.13): every falling edge, every rising
u(t)
Clock
PWM Low-pass y(t)
PWM filter Analog Actuators Process
signal
signal
CPU
x = f(x,u)
u = .......
Low-pass Sensors
A/D
Analog filter PWM
signal signal
Digital controller
FIGURE 4.11: PWM signal to analog voltage conversion in an embedded control system.