Page 242 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 242
228 MECHATRONICS
I/O
Clock Peripherals
u(t) y(t)
PWM Actuators Process
PWM
signal
CPU
x = f(x,u)
u =.......
Timer Sensors
PWM
signal
Digital controller
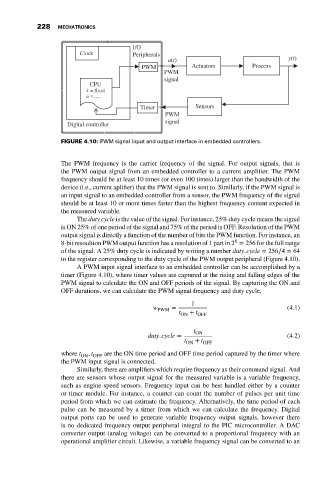
FIGURE 4.10: PWM signal input and output interface in embedded controllers.
The PWM frequency is the carrier frequency of the signal. For output signals, that is
the PWM output signal from an embedded controller to a current amplifier. The PWM
frequency should be at least 10 times (or even 100 times) larger than the bandwidth of the
device (i.e., current aplifier) that the PWM signal is sent to. Similarly, if the PWM signal is
an input signal to an embedded controller from a sensor, the PWM frequency of the signal
should be at least 10 or more times faster than the highest frequency content expected in
the measured variable.
The duty cycle is the value of the signal. For instance, 25% duty cycle means the signal
is ON 25% of one period of the signal and 75% of the period is OFF. Resolution of the PWM
output signal is directly a function of the number of bits the PWM function. For instance, an
8
8-bit resoultion PWM output function has a resolution of 1 part in 2 = 256 for the full range
of the signal. A 25% duty cycle is indicated by writing a number duty cycle = 256∕4 = 64
to the register corresponding to the duty cycle of the PWM output peripheral (Figure 4.10).
A PWM input signal interface to an embedded controller can be accomplished by a
timer (Figure 4.10), where timer values are captured at the rising and falling edges of the
PWM signal to calculate the ON and OFF periods of the signal. By capturing the ON and
OFF durations, we can calculate the PWM signal frequency and duty cycle,
1
w = (4.1)
PWM
t + t
ON OFF
t ON
duty cycle = (4.2)
t ON + t OFF
where t , t are the ON time period and OFF time period captured by the timer where
ON OFF
the PWM input signal is connected.
Similarly, there are amplifiers which require frequency as their command signal. And
there are sensors whose output signal for the measured variable is a variable frequency,
such as engine speed sensors. Frequency input can be best handled either by a counter
or timer module. For instance, a counter can count the number of pulses per unit time
period from which we can estimate the frequency. Alternatively, the time period of each
pulse can be measured by a timer from which we can calculate the frequency. Digital
output ports can be used to generate variable frequency output signals, however there
is no dedicated frequency output peripheral integral to the PIC microcontroller. A DAC
converter output (analog voltage) can be converted to a proportional frequency with an
operational amplifier circuit. Likewise, a variable frequency signal can be converted to an