Page 278 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 278
JWST499-Cetinkunt
JWST499-c05
264 MECHATRONICS Printer: Yet to Come October 28, 2014 11:15 254mm×178mm
i
D
Reverse Reverse Forward Forward
i breakdown bias bias breakdown
D
region region region region
V Z
+ _
V V
V F D
D
(a)
i i
S
L
R i
S Z
_ V
+ S V
V L
V Z R
D L
(b)
Voltage
regulator
A i
AK
A i
G
P i
n AK V RB
Gate (G) V A
P V
G K V AK
n FB
K
K
(c)
i
AK
A
i
i G
AK
–V FB
G V V
AK V AK
FB
K
(d)
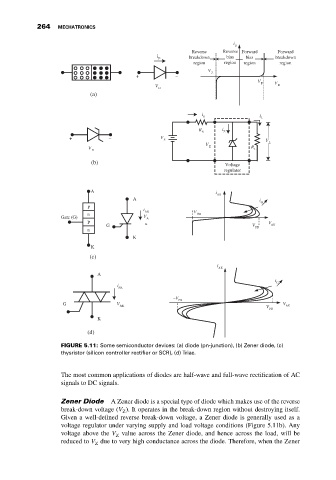
FIGURE 5.11: Some semiconductor devices: (a) diode (pn-junction), (b) Zener diode, (c)
thysristor (silicon controller rectifier or SCR), (d) Triac.
The most common applications of diodes are half-wave and full-wave rectification of AC
signals to DC signals.
Zener Diode A Zener diode is a special type of diode which makes use of the reverse
break-down voltage (V ). It operates in the break-down region without destroying itself.
Z
Given a well-defined reverse break-down voltage, a Zener diode is generally used as a
voltage regulator under varying supply and load voltage conditions (Figure 5.11b). Any
voltage above the V value across the Zener diode, and hence across the load, will be
Z
reduced to V due to very high conductance across the diode. Therefore, when the Zener
Z