Page 286 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 286
JWST499-Cetinkunt
JWST499-c05
272 MECHATRONICS Printer: Yet to Come October 28, 2014 11:15 254mm×178mm
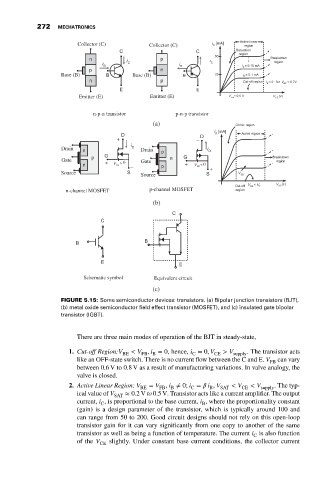
Collector (C) Collector (C)
Base (B) Base (B)
Emitter (E) Emitter (E)
n-p-n transistor p-n-p transistor
(a)
+ –
Drain Drain
Gate Gate
+ 0 + 0
– +
Source Source
n-channel MOSFET p-channel MOSFET
(b)
Schematic symbol Equivalent circuit
(c)
FIGURE 5.15: Some semiconductor devices: transistors. (a) Bipolar junction transistors (BJT),
(b) metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET), and (c) insulated gate bipolar
transistor (IGBT).
There are three main modes of operation of the BJT in steady-state,
1. Cut-off Region:V < V , i = 0, hence, i = 0, V > V . The transistor acts
BE FB B C CE supply
like an OFF-state switch. There is no current flow between the C and E. V can vary
FB
between 0.6V to 0.8 V as a result of manufacturing variations. In valve analogy, the
valve is closed.
2. Active Linear Region: V = V , i ≠ 0; i = i , V < V < V . The typ-
BE FB B C B SAT CE supply
ical value of V ≈ 0.2V to 0.5 V. Transistor acts like a current amplifier. The output
SAT
current, i , is proportional to the base current, i , where the proportionality constant
C
B
(gain) is a design parameter of the transistor, which is typically around 100 and
can range from 50 to 200. Good circuit designs should not rely on this open-loop
transistor gain for it can vary significantly from one copy to another of the same
transistor as well as being a function of temperature. The current i is also function
C
of the V CE slightly. Under constant base current conditions, the collector current