Page 417 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 417
JWST499-Cetinkunt
October 9, 2014 8:1
JWST499-c06
Printer: Yet to Come
SENSORS 403 254mm×178mm
GPS satellites
Machine
Base station (Office)
Radio repeater
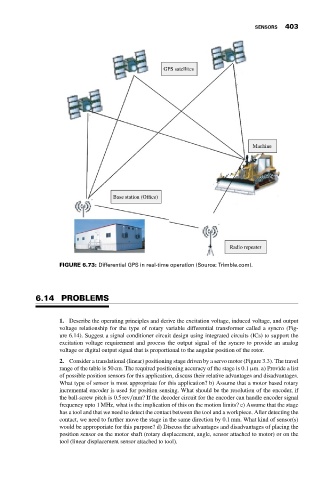
FIGURE 6.73: Differential GPS in real-time operation (Source: Trimble.com).
6.14 PROBLEMS
1. Describe the operating principles and derive the excitation voltage, induced voltage, and output
voltage relationship for the type of rotary variable differential transformer called a syncro (Fig-
ure 6.14). Suggest a signal conditioner circuit design using integrated circuits (ICs) to support the
excitation voltage requirement and process the output signal of the syncro to provide an analog
voltage or digital output signal that is proportional to the angular position of the rotor.
2. Consider a translational (linear) positioning stage driven by a servo motor (Figure 3.3). The travel
range of the table is 50 cm. The required positioning accuracy of the stage is 0.1 μm. a) Provide a list
of possible position sensors for this application, discuss their relative advantages and disadvantages.
What type of sensor is most appropriate for this application? b) Assume that a motor based rotary
incremental encoder is used for position sensing. What should be the resolution of the encoder, if
the ball-screw pitch is 0.5rev∕mm? If the decoder circuit for the encoder can handle encoder signal
frequency upto 1 MHz, what is the implication of this on the motion limits? c) Assume that the stage
has a tool and that we need to detect the contact between the tool and a workpiece. After detecting the
contact, we need to further move the stage in the same direction by 0.1 mm. What kind of sensor(s)
would be approporiate for this purpose? d) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of placing the
position sensor on the motor shaft (rotary displacement, angle, sensor attached to motor) or on the
tool (linear displacement sensor attached to tool).