Page 210 - Servo Motors and Industrial Control Theory -
P. 210
208 Appendix C
velocity. For this you should find the transfer function of the motor and deter-
mine its time constant from which you can determine the dynamic settling time
of the motor.
Determine the velocity drop when the external torque is applied to the motor. For
a more accurate determination of the dynamic response time consider the induc-
tance and obtain the transfer function again and find the value of the dominant
time constant and hence determine the dynamic settling time. You should note
that the motor can be driven at different speed by changing the input voltage. The
above case is the worst condition when the motor is operated at its maximum
speed.
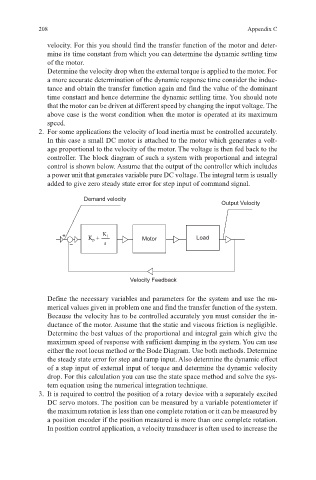
2. For some applications the velocity of load inertia must be controlled accurately.
In this case a small DC motor is attached to the motor which generates a volt-
age proportional to the velocity of the motor. The voltage is then fed back to the
controller. The block diagram of such a system with proportional and integral
control is shown below. Assume that the output of the controller which includes
a power unit that generates variable pure DC voltage. The integral term is usually
added to give zero steady state error for step input of command signal.
Demand velocity
Output Velocity
+ K p + K i Motor Load
– s
Velocity Feedback
Define the necessary variables and parameters for the system and use the nu-
merical values given in problem one and find the transfer function of the system.
Because the velocity has to be controlled accurately you must consider the in-
ductance of the motor. Assume that the static and viscous friction is negligible.
Determine the best values of the proportional and integral gain which give the
maximum speed of response with sufficient damping in the system. You can use
either the root locus method or the Bode Diagram. Use both methods. Determine
the steady state error for step and ramp input. Also determine the dynamic effect
of a step input of external input of torque and determine the dynamic velocity
drop. For this calculation you can use the state space method and solve the sys-
tem equation using the numerical integration technique.
3. It is required to control the position of a rotary device with a separately excited
DC servo motors. The position can be measured by a variable potentiometer if
the maximum rotation is less than one complete rotation or it can be measured by
a position encoder if the position measured is more than one complete rotation.
In position control application, a velocity transducer is often used to increase the