Page 194 - DNBI_A01.QXD
P. 194
171
his light bulb filament, price and continuity of supply were more 5 : STEP THREE – EVALUATING AND SELECTING IDEAS
important than technical performance; for Bezos, width of range and a
fragmented supplier base were the most important criteria in selecting
which product area to pursue.
not all criteria are equal Weighting merely acknowledges that not all
criteria are of equal importance in a given situation and to a given
individual. For some individuals, for example, the ability to work from
home in order to bring up a young family may be the most significant
criterion. For others, it is the degree of financial reward. For yet others,
it may be that keeping risk below a certain threshold, or ease of
implementation, are the key factors.
Your choice of criteria and the weightings which you ascribe to them
depend entirely on you. Weighting requires you to exercise judgement
in ascribing relative weights to the various criteria. A simple solution is
to assign a weighting of 10 to the criterion which you judge to be the
most important and adjust the weighting figures given to the other
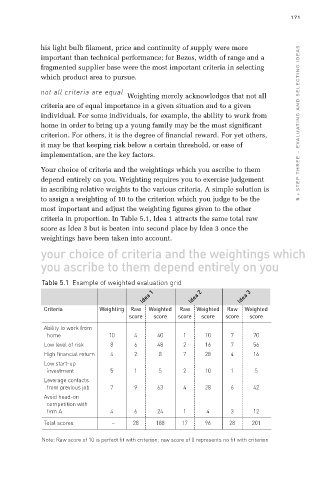
criteria in proportion. In Table 5.1, Idea 1 attracts the same total raw
score as Idea 3 but is beaten into second place by Idea 3 once the
weightings have been taken into account.
your choice of criteria and the weightings which
you ascribe to them depend entirely on you
Table 5.1 Example of weighted evaluation grid
Idea 1
Idea 2
Idea 3
Criteria Weighting Raw Weighted Raw Weighted Raw Weighted
score score score score score score
Ability to work from
home 10 4 40 1 10 7 70
Low level of risk 8 6 48 2 16 7 56
High financial return 4 2 8 7 28 4 16
Low start-up 5 1 5 2 10 1 5
investment
Leverage contacts
from previous job 7 9 63 4 28 6 42
Avoid head-on 4 6 24 1 4 3 12
competition with
firm A
Total scores – 28 188 17 96 28 201
Note: Raw score of 10 is perfect fit with criterion; raw score of 0 represents no fit with criterion