Page 174 - Most-Essential-Learning-Competencies-Matrix-LATEST-EDITION-FROM-BCD
P. 174
174
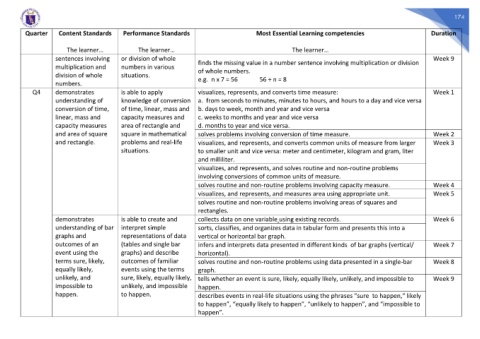
Quarter Content Standards Performance Standards Most Essential Learning competencies Duration
The learner… The learner… The learner…
sentences involving or division of whole Week 9
finds the missing value in a number sentence involving multiplication or division
multiplication and numbers in various
of whole numbers.
division of whole situations. e.g. n x 7 = 56 56 ÷ n = 8
numbers.
Q4 demonstrates is able to apply visualizes, represents, and converts time measure: Week 1
understanding of knowledge of conversion a. from seconds to minutes, minutes to hours, and hours to a day and vice versa
conversion of time, of time, linear, mass and b. days to week, month and year and vice versa
linear, mass and capacity measures and c. weeks to months and year and vice versa
capacity measures area of rectangle and d. months to year and vice versa.
and area of square square in mathematical solves problems involving conversion of time measure. Week 2
and rectangle. problems and real-life visualizes, and represents, and converts common units of measure from larger Week 3
situations. to smaller unit and vice versa: meter and centimeter, kilogram and gram, liter
and milliliter.
visualizes, and represents, and solves routine and non-routine problems
involving conversions of common units of measure.
solves routine and non-routine problems involving capacity measure. Week 4
visualizes, and represents, and measures area using appropriate unit. Week 5
solves routine and non-routine problems involving areas of squares and
rectangles.
demonstrates is able to create and collects data on one variable using existing records. Week 6
understanding of bar interpret simple sorts, classifies, and organizes data in tabular form and presents this into a
graphs and representations of data vertical or horizontal bar graph.
outcomes of an (tables and single bar infers and interprets data presented in different kinds of bar graphs (vertical/ Week 7
event using the graphs) and describe horizontal).
terms sure, likely, outcomes of familiar solves routine and non-routine problems using data presented in a single-bar Week 8
equally likely, events using the terms graph.
unlikely, and sure, likely, equally likely, tells whether an event is sure, likely, equally likely, unlikely, and impossible to Week 9
impossible to unlikely, and impossible happen.
happen. to happen. describes events in real-life situations using the phrases “sure to happen,“ likely
to happen”, “equally likely to happen”, “unlikely to happen”, and “impossible to
happen”.