Page 541 - Most-Essential-Learning-Competencies-Matrix-LATEST-EDITION-FROM-BCD
P. 541
541
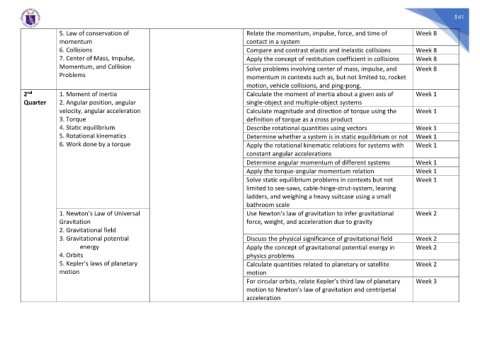
5. Law of conservation of Relate the momentum, impulse, force, and time of Week 8
momentum contact in a system
6. Collisions Compare and contrast elastic and inelastic collisions Week 8
7. Center of Mass, Impulse, Apply the concept of restitution coefficient in collisions Week 8
Momentum, and Collision Solve problems involving center of mass, impulse, and Week 8
Problems momentum in contexts such as, but not limited to, rocket
motion, vehicle collisions, and ping-pong.
nd
2 1. Moment of inertia Calculate the moment of inertia about a given axis of Week 1
Quarter 2. Angular position, angular single-object and multiple-object systems
velocity, angular acceleration Calculate magnitude and direction of torque using the Week 1
3. Torque definition of torque as a cross product
4. Static equilibrium Describe rotational quantities using vectors Week 1
5. Rotational kinematics Determine whether a system is in static equilibrium or not Week 1
6. Work done by a torque Apply the rotational kinematic relations for systems with Week 1
constant angular accelerations
Determine angular momentum of different systems Week 1
Apply the torque-angular momentum relation Week 1
Solve static equilibrium problems in contexts but not Week 1
limited to see-saws, cable-hinge-strut-system, leaning
ladders, and weighing a heavy suitcase using a small
bathroom scale
1. Newton’s Law of Universal Use Newton’s law of gravitation to infer gravitational Week 2
Gravitation force, weight, and acceleration due to gravity
2. Gravitational field
3. Gravitational potential Discuss the physical significance of gravitational field Week 2
energy Apply the concept of gravitational potential energy in Week 2
4. Orbits physics problems
5. Kepler’s laws of planetary Calculate quantities related to planetary or satellite Week 2
motion motion
For circular orbits, relate Kepler’s third law of planetary Week 3
motion to Newton’s law of gravitation and centripetal
acceleration