Page 539 - Most-Essential-Learning-Competencies-Matrix-LATEST-EDITION-FROM-BCD
P. 539
539
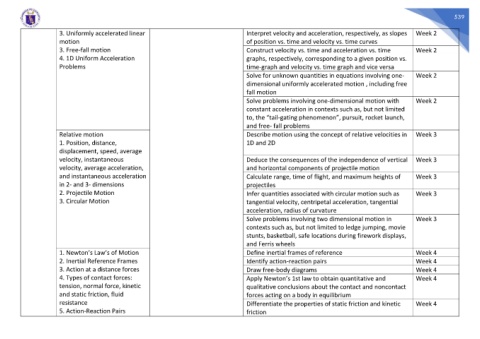
3. Uniformly accelerated linear Interpret velocity and acceleration, respectively, as slopes Week 2
motion of position vs. time and velocity vs. time curves
3. Free-fall motion Construct velocity vs. time and acceleration vs. time Week 2
4. 1D Uniform Acceleration graphs, respectively, corresponding to a given position vs.
Problems time-graph and velocity vs. time graph and vice versa
Solve for unknown quantities in equations involving one- Week 2
dimensional uniformly accelerated motion , including free
fall motion
Solve problems involving one-dimensional motion with Week 2
constant acceleration in contexts such as, but not limited
to, the “tail-gating phenomenon”, pursuit, rocket launch,
and free- fall problems
Relative motion Describe motion using the concept of relative velocities in Week 3
1. Position, distance, 1D and 2D
displacement, speed, average
velocity, instantaneous Deduce the consequences of the independence of vertical Week 3
velocity, average acceleration, and horizontal components of projectile motion
and instantaneous acceleration Calculate range, time of flight, and maximum heights of Week 3
in 2- and 3- dimensions projectiles
2. Projectile Motion Infer quantities associated with circular motion such as Week 3
3. Circular Motion tangential velocity, centripetal acceleration, tangential
acceleration, radius of curvature
Solve problems involving two dimensional motion in Week 3
contexts such as, but not limited to ledge jumping, movie
stunts, basketball, safe locations during firework displays,
and Ferris wheels
1. Newton’s Law’s of Motion Define inertial frames of reference Week 4
2. Inertial Reference Frames Identify action-reaction pairs Week 4
3. Action at a distance forces Draw free-body diagrams Week 4
4. Types of contact forces: Apply Newton’s 1st law to obtain quantitative and Week 4
tension, normal force, kinetic qualitative conclusions about the contact and noncontact
and static friction, fluid forces acting on a body in equilibrium
resistance Differentiate the properties of static friction and kinetic Week 4
5. Action-Reaction Pairs friction