Page 51 - Nature Of Space And Time
P. 51
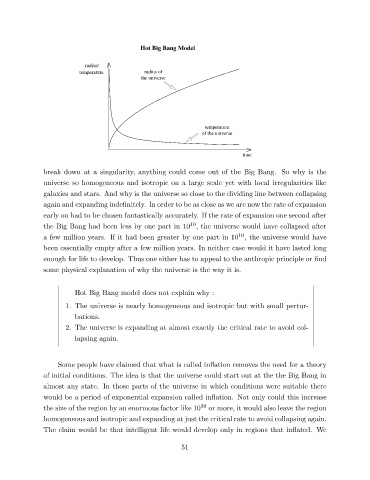
Hot Big Bang Model
radius/
temperature radius of
the universe
temperature
of the universe
time
break down at a singularity, anything could come out of the Big Bang. So why is the
universe so homogeneous and isotropic on a large scale yet with local irregularities like
galaxies and stars. And why is the universe so close to the dividing line between collapsing
again and expanding inde nitely. In order to be as close as we are now the rate of expansion
early on had to be chosen fantastically accurately. If the rate of expansion one second after
10
the Big Bang had been less by one part in 10 , the universe would have collapsed after
10
a few million years. If it had been greater by one part in 10 , the universe would have
been essentially empty after a few million years. In neither case would it have lasted long
enough for life to develop. Thus one either has to appeal to the anthropic principle or nd
some physical explanation of why the universe is the way it is.
Hot Big Bang model does not explain why :
1. The universe is nearly homogeneous and isotropic but with small pertur-
bations.
2. The universe is expanding at almost exactly the critical rate to avoid col-
lapsing again.
Some people have claimed that what is called in
ation removes the need for a theory
of initial conditions. The idea is that the universe could start out at the the Big Bang in
almost any state. In those parts of the universe in which conditions were suitable there
would be a period of exponential expansion called in
ation. Not only could this increase
the size of the region by an enormous factor like 10 30 or more, it would also leave the region
homogeneous and isotropic and expanding at just the critical rate to avoid collapsing again.
The claim would be that intelligent life would develop only in regions that in
ated. We
51