Page 80 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 80
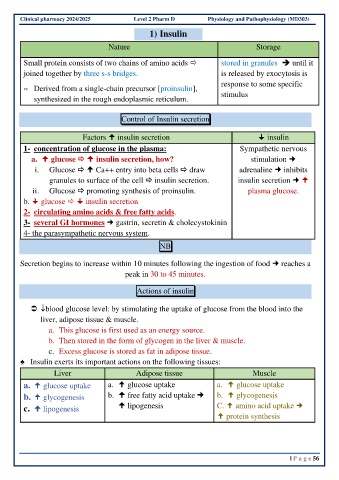
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
1) Insulin
Nature Storage
Small protein consists of two chains of amino acids stored in granules ➔ until it
joined together by three s-s bridges. is released by exocytosis is
response to some specific
Derived from a single-chain precursor [proinsulin],
synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. stimulus
Control of Insulin secretion
Factors insulin secretion insulin
1- concentration of glucose in the plasma: Sympathetic nervous
a. glucose insulin secretion, how? stimulation
i. Glucose Ca++ entry into beta cells draw adrenaline inhibits
granules to surface of the cell insulin secretion. insulin secretion
ii. Glucose promoting synthesis of proinsulin. plasma glucose.
b. glucose insulin secretion
2- circulating amino acids & free fatty acids.
3- several GI hormones gastrin, secretin & cholecystokinin
4- the parasympathetic nervous system.
NB
Secretion begins to increase within 10 minutes following the ingestion of food reaches a
peak in 30 to 45 minutes.
Actions of insulin
blood glucose level: by stimulating the uptake of glucose from the blood into the
liver, adipose tissue & muscle.
a. This glucose is first used as an energy source.
b. Then stored in the form of glycogen in the liver & muscle.
c. Excess glucose is stored as fat in adipose tissue.
♠ Insulin exerts its important actions on the following tissues:
Liver Adipose tissue Muscle
a. glucose uptake a. glucose uptake a. glucose uptake
b. glycogenesis b. free fatty acid uptake b. glycogenesis
c. lipogenesis lipogenesis C. amino acid uptake
protein synthesis
| P a g e 56