Page 84 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 84
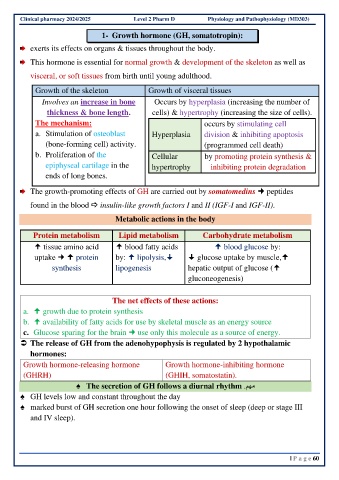
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
1- Growth hormone (GH, somatotropin):
exerts its effects on organs & tissues throughout the body.
This hormone is essential for normal growth & development of the skeleton as well as
visceral, or soft tissues from birth until young adulthood.
Growth of the skeleton Growth of visceral tissues
Involves an increase in bone Occurs by hyperplasia (increasing the number of
thickness & bone length. cells) & hypertrophy (increasing the size of cells).
The mechanism: occurs by stimulating cell
a. Stimulation of osteoblast Hyperplasia division & inhibiting apoptosis
(bone-forming cell) activity. (programmed cell death)
b. Proliferation of the Cellular by promoting protein synthesis &
epiphyseal cartilage in the hypertrophy inhibiting protein degradation
ends of long bones.
The growth-promoting effects of GH are carried out by somatomedins peptides
found in the blood insulin-like growth factors I and II (IGF-I and IGF-II).
Metabolic actions in the body
Protein metabolism Lipid metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism
tissue amino acid blood fatty acids blood glucose by:
uptake protein by: lipolysis, glucose uptake by muscle,
synthesis lipogenesis hepatic output of glucose (
gluconeogenesis)
The net effects of these actions:
a. growth due to protein synthesis
b. availability of fatty acids for use by skeletal muscle as an energy source
c. Glucose sparing for the brain use only this molecule as a source of energy.
The release of GH from the adenohypophysis is regulated by 2 hypothalamic
hormones:
Growth hormone-releasing hormone Growth hormone-inhibiting hormone
(GHRH) (GHIH, somatostatin).
♠ The secretion of GH follows a diurnal rhythm مهم
.
♠ GH levels low and constant throughout the day
♠ marked burst of GH secretion one hour following the onset of sleep (deep or stage III
and IV sleep).
| P a g e 60