Page 85 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 85
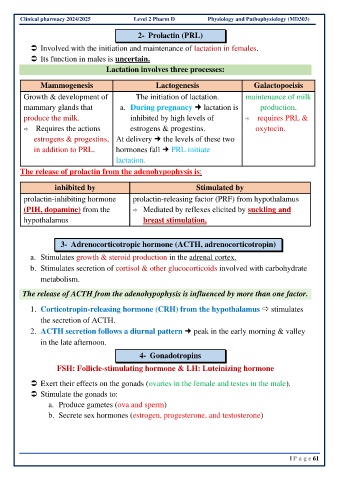
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
2- Prolactin (PRL)
Involved with the initiation and maintenance of lactation in females.
Its function in males is uncertain.
Lactation involves three processes:
Mammogenesis Lactogenesis Galactopoeisis
Growth & development of The initiation of lactation. maintenance of milk
mammary glands that a. During pregnancy lactation is production.
produce the milk. inhibited by high levels of requires PRL &
Requires the actions estrogens & progestins. oxytocin.
estrogens & progestins, At delivery the levels of these two
in addition to PRL. hormones fall PRL initiate
lactation.
The release of prolactin from the adenohypophysis is:
inhibited by Stimulated by
prolactin-inhibiting hormone prolactin-releasing factor (PRF) from hypothalamus
(PIH, dopamine) from the Mediated by reflexes elicited by suckling and
hypothalamus breast stimulation.
3- Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH, adrenocorticotropin)
a. Stimulates growth & steroid production in the adrenal cortex.
b. Stimulates secretion of cortisol & other glucocorticoids involved with carbohydrate
metabolism.
The release of ACTH from the adenohypophysis is influenced by more than one factor.
1. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates
the secretion of ACTH.
2. ACTH secretion follows a diurnal pattern peak in the early morning & valley
in the late afternoon.
4- Gonadotropins
FSH: Follicle-stimulating hormone & LH: Luteinizing hormone
Exert their effects on the gonads (ovaries in the female and testes in the male).
Stimulate the gonads to:
a. Produce gametes (ova and sperm)
b. Secrete sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone)
| P a g e 61