Page 81 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 81
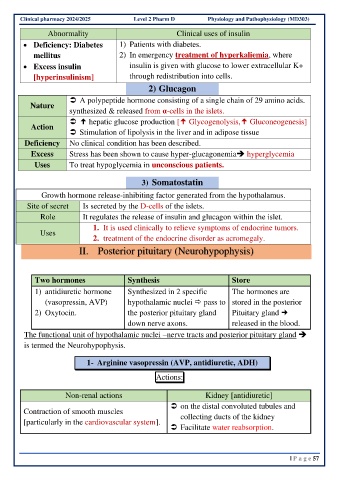
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
Abnormality Clinical uses of insulin
• Deficiency: Diabetes 1) Patients with diabetes.
mellitus 2) In emergency treatment of hyperkaliemia, where
• Excess insulin insulin is given with glucose to lower extracellular K+
[hyperinsulinism] through redistribution into cells.
2) Glucagon
A polypeptide hormone consisting of a single chain of 29 amino acids.
Nature
synthesized & released from α-cells in the islets.
hepatic glucose production [ Glycogenolysis, Gluconeogenesis]
Action
Stimulation of lipolysis in the liver and in adipose tissue
Deficiency No clinical condition has been described.
Excess Stress has been shown to cause hyper-glucagonemia➔ hyperglycemia
Uses To treat hypoglycemia in unconscious patients.
3) Somatostatin
Growth hormone release-inhibiting factor generated from the hypothalamus.
Site of secret Is secreted by the D-cells of the islets.
Role It regulates the release of insulin and glucagon within the islet.
1. It is used clinically to relieve symptoms of endocrine tumors.
Uses
2. treatment of the endocrine disorder as acromegaly.
II. Posterior pituitary (Neurohypophysis)
Two hormones Synthesis Store
1) antidiuretic hormone Synthesized in 2 specific The hormones are
(vasopressin, AVP) hypothalamic nuclei pass to stored in the posterior
2) Oxytocin. the posterior pituitary gland Pituitary gland
down nerve axons. released in the blood.
The functional unit of hypothalamic nuclei –nerve tracts and posterior pituitary gland ➔
is termed the Neurohypophysis.
1- Arginine vasopressin (AVP, antidiuretic, ADH)
Actions:
Non-renal actions Kidney [antidiuretic]
on the distal convoluted tubules and
Contraction of smooth muscles collecting ducts of the kidney
[particularly in the cardiovascular system].
Facilitate water reabsorption.
| P a g e 57