Page 87 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 87
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
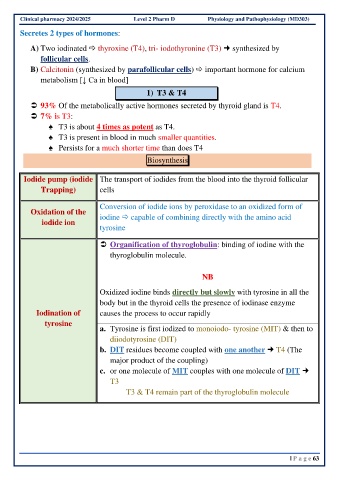
Secretes 2 types of hormones:
A) Two iodinated thyroxine (T4), tri- iodothyronine (T3) synthesized by
follicular cells.
B) Calcitonin (synthesized by parafollicular cells) important hormone for calcium
metabolism [↓ Ca in blood]
1) T3 & T4
93% Of the metabolically active hormones secreted by thyroid gland is T4.
7% is T3:
♠ T3 is about 4 times as potent as T4.
♠ T3 is present in blood in much smaller quantities.
♠ Persists for a much shorter time than does T4
Biosynthesis
Iodide pump (iodide The transport of iodides from the blood into the thyroid follicular
Trapping) cells
Conversion of iodide ions by peroxidase to an oxidized form of
Oxidation of the iodine capable of combining directly with the amino acid
iodide ion
tyrosine
Organification of thyroglobulin: binding of iodine with the
thyroglobulin molecule.
NB
Oxidized iodine binds directly but slowly with tyrosine in all the
body but in the thyroid cells the presence of iodinase enzyme
Iodination of causes the process to occur rapidly
tyrosine
a. Tyrosine is first iodized to monoiodo- tyrosine (MIT) & then to
diiodotyrosine (DIT)
b. DIT residues become coupled with one another T4 (The
major product of the coupling)
c. or one molecule of MIT couples with one molecule of DIT
T3
T3 & T4 remain part of the thyroglobulin molecule
| P a g e 63