Page 92 - Physiology and Pathophysiology MNU 2024-2025 نظرى
P. 92
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 2 Pharm D Physiology and Pathophysiology (MD303)
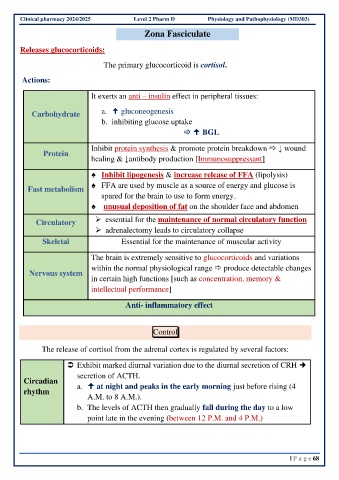
Zona Fasciculate
Releases glucocorticoids:
The primary glucocorticoid is cortisol.
Actions:
It exerts an anti – insulin effect in peripheral tissues:
Carbohydrate a. gluconeogenesis
b. inhibiting glucose uptake
BGL
Inhibit protein synthesis & promote protein breakdown ↓ wound
Protein
healing & ↓antibody production [Immunosuppressant]
♠ Inhibit lipogenesis & increase release of FFA (lipolysis)
♠ FFA are used by muscle as a source of energy and glucose is
Fast metabolism
spared for the brain to use to form energy.
♠ unusual deposition of fat on the shoulder face and abdomen
Circulatory ➢ essential for the maintenance of normal circulatory function
➢ adrenalectomy leads to circulatory collapse
Skeletal Essential for the maintenance of muscular activity
The brain is extremely sensitive to glucocorticoids and variations
within the normal physiological range produce detectable changes
Nervous system
in certain high functions [such as concentration, memory &
intellectual performance]
Anti- inflammatory effect
Control
The release of cortisol from the adrenal cortex is regulated by several factors:
Exhibit marked diurnal variation due to the diurnal secretion of CRH
secretion of ACTH.
Circadian
rhythm a. at night and peaks in the early morning just before rising (4
A.M. to 8 A.M.).
b. The levels of ACTH then gradually fall during the day to a low
point late in the evening (between 12 P.M. and 4 P.M.)
| P a g e 68