Page 67 - pharma 1 theoretical updated MNU_Neat
P. 67
Clinical pharmacy 2024/2025 Level 3 Pharm D Pharmacology 1 (PO 502)
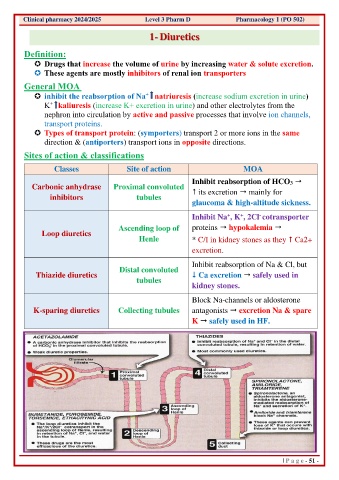
1- Diuretics
Definition:
Drugs that increase the volume of urine by increasing water & solute excretion.
These agents are mostly inhibitors of renal ion transporters
General MOA
+
inhibit the reabsorption of Na natriuresis (increase sodium excretion in urine)
+
K kaliuresis (increase K+ excretion in urine) and other electrolytes from the
nephron into circulation by active and passive processes that involve ion channels,
transport proteins.
Types of transport protein: (symporters) transport 2 or more ions in the same
direction & (antiporters) transport ions in opposite directions.
Sites of action & classifications
Classes Site of action MOA
Inhibit reabsorption of HCO3
Carbonic anhydrase Proximal convoluted its excretion mainly for
inhibitors tubules
glaucoma & high-altitude sickness.
Inhibit Na , K , 2Cl cotransporter
+
-
+
Ascending loop of proteins hypokalemia
Loop diuretics
Henle * C/I in kidney stones as they Ca2+
excretion.
Inhibit reabsorption of Na & Cl, but
Distal convoluted
Thiazide diuretics Ca excretion safely used in
tubules
kidney stones.
Block Na-channels or aldosterone
K-sparing diuretics Collecting tubules antagonists excretion Na & spare
K safely used in HF.
| P a g e - 51 -