Page 228 - FBL AR 2019-20
P. 228
Fermenta Biotech Limited
Annual Report 2019-20
Notes to the Consolidated financial statements for the year ended March 31, 2020
56 Financial risk management objectives and policies (contd.)
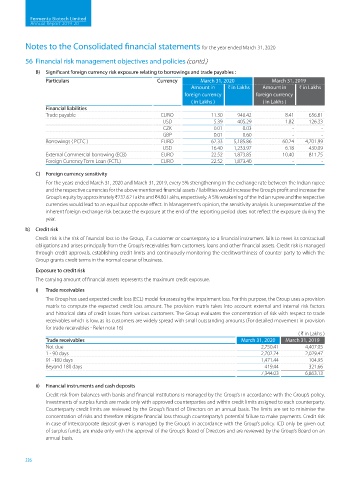
B) Significant foreign currency risk exposure relating to borrowings and trade payables :
Particulars Currency March 31, 2020 March 31, 2019
Amount in H in Lakhs Amount in H in Lakhs
foreign currency foreign currency
( in Lakhs ) ( in Lakhs )
Financial liabilities
Trade payable EURO 11.30 940.42 8.41 656.81
USD 5.39 405.29 1.82 126.33
CZK 0.01 0.03 - -
GBP 0.01 0.60 - -
Borrowings ( PCFC ) EURO 62.33 5,185.86 60.24 4,701.99
USD 16.40 1,233.97 6.18 430.09
External Commercial borrowing (ECB) EURO 22.52 1,873.85 10.40 811.75
Foreign Currency Term Loan (FCTL) EURO 22.52 1,873.40 - -
C) Foreign currency sensitivity
For the years ended March 31, 2020 and March 31, 2019, every 5% strengthening in the exchange rate between the Indian rupee
and the respective currencies for the above mentioned financial assets / liabilities would increase the Group’s profit and increase the
Group’s equity by approximately H232.62 Lakhs and H4.80 Lakhs, respectively. A 5% weakening of the Indian rupee and the respective
currencies would lead to an equal but opposite effect. In Management’s opinion, the sensitivity analysis is unrepresentative of the
inherent foreign exchange risk because the exposure at the end of the reporting period does not reflect the exposure during the
year.
b) Credit risk
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Group, if a customer or counterparty to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual
obligations and arises principally from the Group’s receivables from customers, loans and other financial assets. Credit risk is managed
through credit approvals, establishing credit limits and continuously monitoring the creditworthiness of counter party to which the
Group grants credit terms in the normal course of business.
Exposure to credit risk
The carrying amount of financial assets represents the maximum credit exposure.
i) Trade receivables
The Group has used expected credit loss (ECL) model for assessing the impairment loss. For this purpose, the Group uses a provision
matrix to compute the expected credit loss amount. The provision matrix takes into account external and internal risk factors
and historical data of credit losses from various customers. The Group evaluates the concentration of risk with respect to trade
receivables which is low, as its customers are widely spread with small outstanding amounts (For detailed movement in provision
for trade receivables - Refer note 16)
( H in Lakhs )
Trade receivables March 31, 2020 March 31, 2019
Not due 2,750.41 4,407.05
1 - 90 days 2,702.74 2,029.47
91 -180 days 1,471.44 104.95
Beyond 180 days 419.44 321.66
7,344.03 6,863.13
ii) Financial instruments and cash deposits
Credit risk from balances with banks and financial institutions is managed by the Group’s in accordance with the Group’s policy.
Investments of surplus funds are made only with approved counterparties and within credit limits assigned to each counterparty.
Counterparty credit limits are reviewed by the Group’s Board of Directors on an annual basis. The limits are set to minimise the
concentration of risks and therefore mitigate financial loss through counterparty’s potential failure to make payments. Credit risk
in case of Intercorporate deposit given is managed by the Group’s in accordance with the Group’s policy. ICD only be given out
of surplus funds, are made only with the approval of the Group’s Board of Directors and are reviewed by the Group’s Board on an
annual basis.
226