Page 70 - Analytical Chemistry I E-book
P. 70
Titration curves for polyfunctional bases
• Typical example of polyfunctional bases is sodium carbonate (Na2CO3).
Carbonate ion is the conjugate base of carbonic acid, and it is involved in the
following stepwise equilibria: K = 2.13 x 10–4
CO 2– + H O HCO – + OH– Kb1 = 6.70 x 10–11
HCO3 – + H2 O H CO3 + OH–
32 23 b2
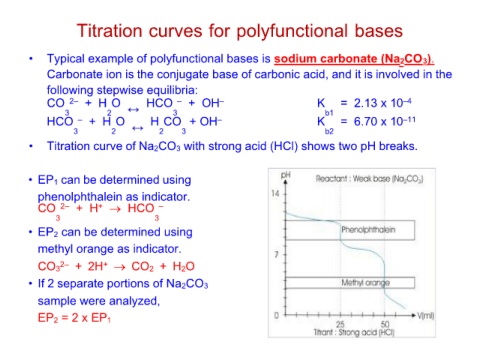
• Titration curve of Na2CO3 with strong acid (HCl) shows two pH breaks.
• EP1 can be determined using
phenolphthalein as indicator.
CO 2– + H+ → HCO –
33
• EP2 can be determined using
methyl orange as indicator.
CO32– + 2H+ → CO2 + H2O
• If 2 separate portions of Na2CO3
sample were analyzed,
EP2 = 2 x EP1