Page 57 - phytochemistry II -pharmD general
P. 57
I- Solanaceous tropane alkaloids
The term solanaceous alkaloids is generally restricted to the alkaloids of the
tropane nucleus, although a number of some genera of the family Solanaceae
contain non-tropane alkaloids e.g. capsaicine, solanine, nicotine etc. Because of
their mydriatic effect, the tropane solanaceous alkaloids are also referred to as
“mydriatic alkaloids”.
Plant source
The most important solanaceous plants that contain tropane alkaloids are
species of the genera, Atropa, Datura, Hyoscyamus, Duboisia, Scopolia and
Anisodus.
There are considerable variations in alkaloidal contents among different
plants of the same genus e.g. Datura species, D. stramonium, D. tatula, D.
sanguinea accumulate more hyoscyamine than scopolamine. On the other hand,
D. metel, D. ferox, D. innoxia, D. arborea accumulate more scopolamine than
hyoscyamine.
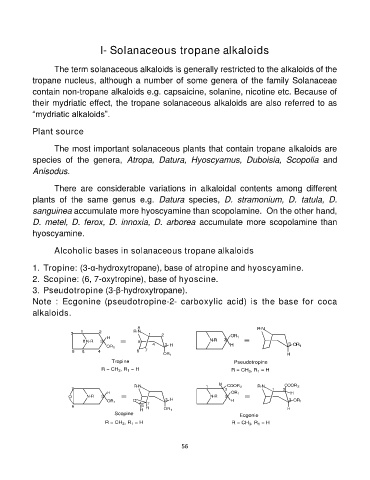
Alcoholic bases in solanaceous tropane alkaloids
1. Tropine: (3-α-hydroxytropane), base of atropine and hyoscyamine.
2. Scopine: (6, 7-oxytropine), base of hyoscine.
3. Pseudotropine (3-β-hydroxytropane).
Note : Ecgonine (pseudotropine-2- carboxylic acid) is the base for coca
alkaloids.
71 2 8 R-N
R-N
8 N-R 3 H 2 N-R 3 OR1
1 3H H
OR1 OR1 3 OR1
65 4 5 H
4
67
Tropine Pseudotropine
R = CH3, R1 = H
R = CH3, R1 = H
7 R-N 1 H COOR 2 R-N COOR 2
2 1 2
H OR1
O N-R 3 3H H
OR1 N-R 3 3 OR1
OR1 O 7 H
H H
6 6
H
Scopine
Ecgonie
R = CH3, R1 = H R = CH3, R1 = H
56