Page 55 - Pharmd general phytochemistry I-Final2024_LEUCTERS
P. 55
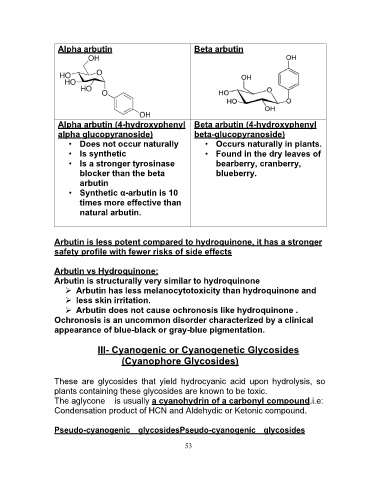
Alpha arbutin Beta arbutin
Alpha arbutin (4-hydroxyphenyl Beta arbutin (4-hydroxyphenyl
alpha glucopyranoside) beta-glucopyranoside)
• Does not occur naturally • Occurs naturally in plants.
• Is synthetic
• Found in the dry leaves of
• Is a stronger tyrosinase bearberry, cranberry,
blocker than the beta blueberry.
arbutin
• Synthetic α-arbutin is 10
times more effective than
natural arbutin.
Arbutin is less potent compared to hydroquinone, it has a stronger
safety profile with fewer risks of side effects
Arbutin vs Hydroquinone:
Arbutin is structurally very similar to hydroquinone
Arbutin has less melanocytotoxicity than hydroquinone and
less skin irritation.
Arbutin does not cause ochronosis like hydroquinone .
Ochronosis is an uncommon disorder characterized by a clinical
appearance of blue-black or gray-blue pigmentation.
III- Cyanogenic or Cyanogenetic Glycosides
(Cyanophore Glycosides)
These are glycosides that yield hydrocyanic acid upon hydrolysis, so
plants containing these glycosides are known to be toxic.
The aglycone is usually a cyanohydrin of a carbonyl compound.i.e:
Condensation product of HCN and Aldehydic or Ketonic compound.
Pseudo-cyanogenic glycosidesPseudo-cyanogenic glycosides
53