Page 63 - Pharmaceutical Analytical Chemistry II - Pharm D Clinical- 07-PA202
P. 63
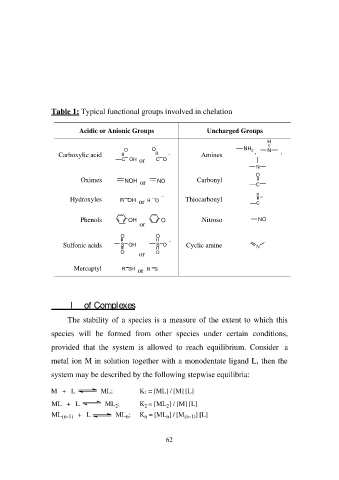
Table 1: Typical functional groups involved in chelation
Acidic or Anionic Groups Uncharged Groups
Carboxylic acid OO Amines NH2 , H ,
N
C OH or C O
Oximes NOH or NO Carbonyl N
Hydroxyles O
Phenols C
Sulfonic acids R OH or R O Thiocarbonyl S
Mercaptyl C
OH O Nitroso NO
or O Cyclic amine N
SO
O O
S OH
O or
R SH or R S
Stability of Complexes
The stability of a species is a measure of the extent to which this
species will be formed from other species under certain conditions,
provided that the system is allowed to reach equilibrium. Consider a
metal ion M in solution together with a monodentate ligand L, then the
system may be described by the following stepwise equilibria:
M+L ML; K1 = [ML] / [M] [L]
ML + L
ML(n-1) + L ML2; K2 = [ML2] / [M] [L]
MLn; Kn = [MLn] / [M(n-1)] [L]
62