Page 37 - RCM - A practical Guide_V1
P. 37
RCM - A Practical Guide
Task selection
Once OC maintenance has been identified as applicable, and the analysis understands the potential
failure condition, it must then design the task itself and it will consider all techniques capable of
detecting the potential failure condition.
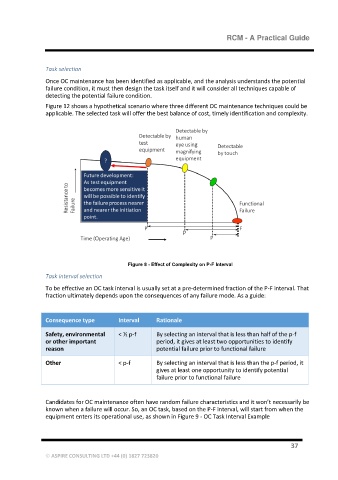
Figure 12 shows a hypothetical scenario where three different OC maintenance techniques could be
applicable. The selected task will offer the best balance of cost, timely identification and complexity.
Figure 8 - Effect of Complexity on P-F Interval
Task interval selection
To be effective an OC task interval is usually set at a pre-determined fraction of the P-F interval. That
fraction ultimately depends upon the consequences of any failure mode. As a guide:
Consequence type Interval Rationale
Safety, environmental < ½ p-f By selecting an interval that is less than half of the p-f
or other important period, it gives at least two opportunities to identify
reason potential failure prior to functional failure
Other < p-f By selecting an interval that is less than the p-f period, it
gives at least one opportunity to identify potential
failure prior to functional failure
Candidates for OC maintenance often have random failure characteristics and it won’t necessarily be
known when a failure will occur. So, an OC task, based on the P-F interval, will start from when the
equipment enters its operational use, as shown in Figure 9 - OC Task Interval Example
37
© ASPIRE CONSULTING LTD +44 (0) 1827 723820