Page 36 - RCM - A practical Guide_V1
P. 36
RCM - A Practical Guide
The main advantage of OC maintenance is that it allows an asset to find its natural life. The asset can
remain in service until a potential failure is detected and then either replaced or some form of repair
made to restore its inherent capability.
Potential failure
A potential failure may be defined as follows:
An identifiable physical condition that indicates that the resistance to failure is reducing and functional
failure is occurring and may be imminent.
The ways in which potential failures manifest themselves are many and varied ranging, for example,
from looseness caused by wear, magnetic particles in oil or simply a loss of performance.
If the loss of function is deemed intolerable, for whatever reason, OC maintenance is effective in
mitigating the consequences because it works to identify (and correct) potential failure conditions
before they deteriorate to functional failure.
The development of Health and Usage Monitoring System (HUMS) makes it possible to constantly
monitor the condition of key items - thus reducing the burden of OC maintenance - to warn of
impending failure. This type of monitoring is commonplace on modern high value equipment and
should be captured in the FMEA to inform this decision-making process.
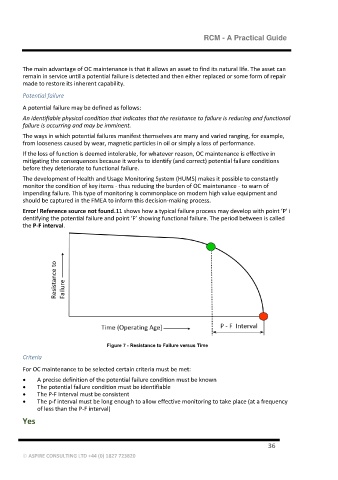
Error! Reference source not found.11 shows how a typical failure process may develop with point ‘P’ i
dentifying the potential failure and point ‘F’ showing functional failure. The period between is called
the P-F interval.
Figure 7 - Resistance to Failure versus Time
Criteria
For OC maintenance to be selected certain criteria must be met:
• A precise definition of the potential failure condition must be known
• The potential failure condition must be identifiable
• The P-F Interval must be consistent
• The p-f interval must be long enough to allow effective monitoring to take place (at a frequency
of less than the P-F interval)
Yes
36
© ASPIRE CONSULTING LTD +44 (0) 1827 723820