Page 18 - Evaluasi Dampak Penghentian Proses Pengadaan Barang dan Jasa DAK Bidang Jalan dan Jembatan
P. 18
of provincial road is still 69%, and district/city road still freedom of as-sociation and speech, as well as on the
is 57% in sta-ble (good and average) condition compare capac-ity to participate constructively.
to na-tional road which is already 92% in stable condi- 2. Rule of law: Legal frameworks should be fair and
tion. For regional road condition, there is a back-log enforced impartially, particularly the laws on human
around 7% of stable condition compare to the national rights.
target, which are 75% and 65% stable for provincial road 3. Transparency: This concept is built on the free flow of
and district/city road, respec-tively. information. Processes, institutions and information
should be directly accessible to those concerned, and
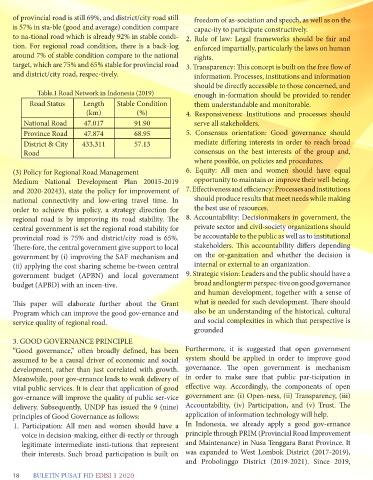
Table.1 Road Network in Indonesia (2019) enough in-formation should be provided to render
Road Status Length Stable Condition them understandable and monitorable.
(km) (%) 4. Responsiveness: Institutions and processes should
National Road 47.017 91.90 serve all stakeholders.
Province Road 47.874 68.95 5. Consensus orientation: Good governance should
District & City 433,311 57.13 mediate differing interests in order to reach broad
Road consensus on the best interests of the group and,
where possible, on policies and procedures.
(3) Policy for Regional Road Management 6. Equity: All men and women should have equal
Medium National Development Plan 20015-2019 opportunity to maintain or improve their well-being.
and 2020-20243), state the policy for improvement of 7. Effectiveness and efficiency: Processes and institutions
national connectivity and low-ering travel time. In should produce results that meet needs while making
order to achieve this policy, a strategy direction for the best use of resources.
regional road is by improving its road stability. The 8. Accountability: Decisionmakers in government, the
central government is set the regional road stability for private sector and civil-society organizations should
provincial road is 75% and district/city road is 65%. be accountable to the public as well as to institutional
There-fore, the central government give support to local stakeholders. This accountability differs depending
government by (i) improving the SAF mechanism and on the or-ganization and whether the decision is
(ii) applying the cost sharing scheme be-tween central internal or external to an organization.
government budget (APBN) and local government 9. Strategic vision: Leaders and the public should have a
budget (APBD) with an incen-tive. broad and longterm perspec-tive on good governance
and human development, together with a sense of
This paper will elaborate further about the Grant what is needed for such development. There should
Program which can improve the good gov-ernance and also be an understanding of the historical, cultural
service quality of regional road. and social complexities in which that perspective is
grounded
3. GOOD GOVERNANCE PRINCIPLE
“Good governance,” often broadly defined, has been Furthermore, it is suggested that open government
assumed to be a causal driver of economic and social system should be applied in order to improve good
development, rather than just correlated with growth. governance. The open government is mechanism
Meanwhile, poor gov-ernance leads to weak delivery of in order to make sure that public par-ticipation in
vital public services. It is clear that application of good effective way. Accordingly, the components of open
gov-ernance will improve the quality of public ser-vice government are: (i) Open-ness, (ii) Transparency, (iii)
delivery. Subsequently, UNDP has issued the 9 (nine) Accountability, (iv) Participation, and (v) Trust. The
principles of Good Governance as follows: application of information technology will help.
1. Participation: All men and women should have a In Indonesia, we already apply a good gov-ernance
voice in decision-making, either di-rectly or through principle through PRIM (Provincial Road Improvement
legitimate intermediate insti-tutions that represent and Maintenance) in Nusa Tenggara Barat Province. It
their interests. Such broad participation is built on was expanded to West Lombok District (2017-2019),
and Probolinggo District (2019-2021). Since 2019,
18 BULETIN PUSAT FID EDISI 1 2020
18