Page 165 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 165
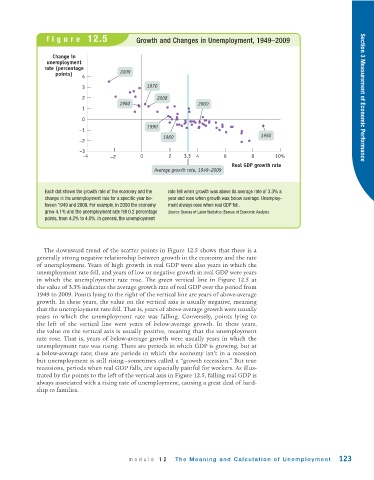
figure 12.5 Growth and Changes in Unemployment, 1949–2009
Change in
unemployment
rate (percentage
points) 4 2009
3 1970
2 2008 Section 3 Measurement of Economic Performance
1980 2000
1
0
1990
–1
1960 1950
–2
–3
–4 –2 0 2 3.3 4 6 8 10%
Real GDP growth rate
Average growth rate, 1949–2009
Each dot shows the growth rate of the economy and the rate fell when growth was above its average rate of 3.3% a
change in the unemployment rate for a specific year be- year and rose when growth was below average. Unemploy-
tween 1949 and 2009. For example, in 2000 the economy ment always rose when real GDP fell.
grew 4.1% and the unemployment rate fell 0.2 percentage Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics; Bureau of Economic Analysis.
points, from 4.2% to 4.0%. In general, the unemployment
The downward trend of the scatter points in Figure 12.5 shows that there is a
generally strong negative relationship between growth in the economy and the rate
of unemployment. Years of high growth in real GDP were also years in which the
unemployment rate fell, and years of low or negative growth in real GDP were years
in which the unemployment rate rose. The green vertical line in Figure 12.5 at
the value of 3.3% indicates the average growth rate of real GDP over the period from
1949 to 2009. Points lying to the right of the vertical line are years of above-average
growth. In these years, the value on the vertical axis is usually negative, meaning
that the unemployment rate fell. That is, years of above -average growth were usually
years in which the unemployment rate was falling. Conversely, points lying to
the left of the vertical line were years of below- average growth. In these years,
the value on the vertical axis is usually positive, meaning that the unemployment
rate rose. That is, years of below -average growth were usually years in which the
unemployment rate was rising. There are periods in which GDP is growing, but at
a below -average rate; these are periods in which the economy isn’t in a recession
but unemployment is still rising—sometimes called a “growth recession.” But true
recessions, periods when real GDP falls, are especially painful for workers. As illus-
trated by the points to the left of the vertical axis in Figure 12.5, falling real GDP is
always associated with a rising rate of unemployment, causing a great deal of hard-
ship to families.
module 12 The Meaning and Calculation of Unemployment 123