Page 653 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 653
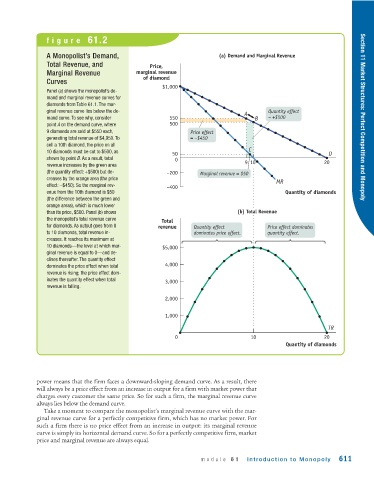
figure 61.2
A Monopolist’s Demand, (a) Demand and Marginal Revenue
Total Revenue, and Price,
Marginal Revenue marginal revenue
of diamond
Curves
$1,000
Panel (a) shows the monopolist’s de-
mand and marginal revenue curves for
diamonds from Table 61.1. The mar-
ginal revenue curve lies below the de- A Quantity effect
mand curve. To see why, consider 550 B = +$500 Section 11 Market Structures: Perfect Competition and Monopoly
point A on the demand curve, where 500
9 diamonds are sold at $550 each, Price effect
generating total revenue of $4,950. To = –$450
sell a 10th diamond, the price on all
C
10 diamonds must be cut to $500, as 50 D
shown by point B. As a result, total 0 910
revenue increases by the green area 20
(the quantity effect: +$500) but de- –200 Marginal revenue = $50
creases by the orange area (the price
MR
effect: −$450). So the marginal rev- –400
enue from the 10th diamond is $50 Quantity of diamonds
(the difference between the green and
orange areas), which is much lower
than its price, $500. Panel (b) shows (b) Total Revenue
the monopolist’s total revenue curve
Total
for diamonds. As output goes from 0 revenue Quantity effect Price effect dominates
to 10 diamonds, total revenue in- dominates price effect. quantity effect.
creases. It reaches its maximum at
10 diamonds—the level at which mar- $5,000
ginal revenue is equal to 0—and de-
clines thereafter. The quantity effect
dominates the price effect when total 4,000
revenue is rising; the price effect dom-
inates the quantity effect when total 3,000
revenue is falling.
2,000
1,000
TR
0 10 20
Quantity of diamonds
power means that the firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve. As a result, there
will always be a price effect from an increase in output for a firm with market power that
charges every customer the same price. So for such a firm, the marginal revenue curve
always lies below the demand curve.
Take a moment to compare the monopolist’s marginal revenue curve with the mar-
ginal revenue curve for a perfectly competitive firm, which has no market power. For
such a firm there is no price effect from an increase in output: its marginal revenue
curve is simply its horizontal demand curve. So for a perfectly competitive firm, market
price and marginal revenue are always equal.
module 61 Introduction to Monopoly 611