Page 66 - e-book CPG - Bipolar Disorder
P. 66
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES MANAGEMENT OF BIPOLAR DISORDER (2ND ED.)
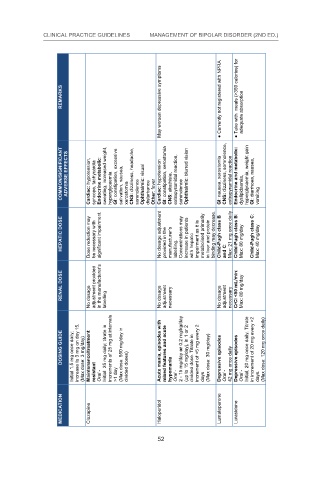
May worsen depressive symptoms adequate absorption
REMARKS ● Currently not registered with NPRA ● Take with meals (>350 calories) for
COMMON/SIGNIFICANT ADVERSE EFFECTS Cardiac: hypotension, syncope, tachycardia Endocrine metabolic: sweating, increased weight, hyperglycaemia GI: constipation, excessive salivation, nausea, xerostomia CNS: dizziness, headache, somnolence Ophthalmic: visual disturbance Other: fever Card
HEPATIC DOSE Dose reduction may be necessary with significant impairment No dosage adjustment provided in the manufacturer’s labelling. Concentrations may increase in patients with hepatic impairment as it is metabolised primarily in liver and protein binding may decrease. Child-Pugh
RENAL DOSE No dosage adjustment provided in the manufacturer’s labelling No dosage adjustment necessary No dosage adjustment necessary CrCl <50 mL/min: Max: 80 mg/day
DOSING GUIDE Initial 1.5 mg once daily; increase to 3 mg on day 15. (Max dose: 3 mg/day) Maintenance/treatment resistant Oral - Initial: 25 mg daily; titrate in increments of 25 mg at intervals >1 day (Max dose: 550 mg/day in divided doses) Acute mania, episodes with mixed features and acute
MEDICATION Clozapine Haloperidol Lurasidone
Lumateperone
52