Page 70 - e-book CPG - Bipolar Disorder
P. 70
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES MANAGEMENT OF BIPOLAR DISORDER (2ND ED.)
Appendix 6
PSYCHOEDUCATION FOR BIPOLAR DISORDER Appendix 6
Appendix 6
Appendix 6
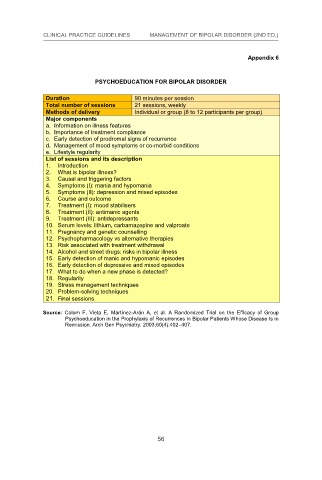
PSYCHOEDUCATION FOR BIPOLAR DISORDER
90 minutes per session
Duration PSYCHOEDUCATION FOR BIPOLAR DISORDER
PSYCHOEDUCATION FOR BIPOLAR DISORDER
Total number of sessions 21 sessions, weekly
Duration 90 minutes per session
Duration
90 minutes per session
Methods of delivery
Individual or group (8 to 12 participants per group)
Duration
90 minutes per session
Total number of sessions
21 sessions, weekly
Total number of sessions
21 sessions, weekly
Major components
Total number of sessions
21 sessions, weekly
Methods of delivery
a. Information on illness features Individual or group (8 to 12 participants per group)
Methods of delivery
Individual or group (8 to 12 participants per group)
Methods of delivery
Major components
Major components
b. Importance of treatment compliance
Major components Individual or group (8 to 12 participants per group)
a. Information on illness features
c. Early detection of prodromal signs of recurrence
a. Information on illness features
b. Importance of treatment compl
a. Information on illness features iance
b. Importance of treatment compliance
d. Management of mood symptoms or co-morbid conditions
c. Early detection of prodromal signs of
b. Importance of treatment compliance recurrence
c. Early detection of prodromal signs of recurrence
e. Lifestyle regularity
c. Early detection of prodromal signs of recurrence
d. Management of mood symptoms or co-morbid conditions
List of sessions and its description
d. Management of mood symptoms or co-morbid conditions
e. Lifestyle regularity
d. Management of mood symptoms or co-morbid conditions
e. Lifestyle regularity
1. Introduction
e. Lifestyle regularity
List of sessions and its description
2. What is bipolar illness? scription
List of sessions and its de
List of sessions and its description
1. Introduction
3. Causal and triggering factors
1. Introduction
1. Introduction
2. What is bipolar illness?
4. Symptoms (I): mania and hypomania
2. What is bipolar illness?
3. Causal and triggering factors
2. What is bipolar illness?
3. Causal and triggering factors
5. Symptoms (II): depression and mixed episodes
3. Causal and triggering factors
4. Symptoms (I): mania and hypomania
6. Course and outcome
4. Symptoms (I): mania and hypomania
5. Symptoms (II): depression and mixed episodes
4. Symptoms (I): mania and hypomania
5. Symptoms (II): depression and
7. Treatment (I): mood stabilisers mixed episodes
5. Symptoms (II): depression and mixed episodes
6. Course and outcome
8. Treatment (II): antimanic agents
6. Course and outcome
6. Course and outcome
7. Treatment (I): mood stabilisers
9. Treatment (III): antidepressants
7. Treatment (I): mood stabilisers
7. Treatment (I): mood stabilisers
8. Treatment (II): antimanic agents
8. Treatment (II): antimanic agents
10. Serum levels: lithium, carbamazepine and valproate
8. Treatment (II): antimanic agents
9. Treatment (III): antidepressants
11. Pregnancy and genetic counselling
9. Treatment (III): antidepressants
9. Treatment (III): antidepressants
10. Serum levels: lithium, carbamazepine and valproate
10. Serum levels: lithium, carbamazepine and valproate
12. Psychopharmacology vs alternative therapies
10. Serum levels: lithium, carbamazepine and valproate
11. Pregnancy and genetic counselling
11. Pregnancy and genetic counselling
13. Risk associated with treatment withdrawal
11. Pregnancy and genetic counselling
12. Psychopharmacology vs alternative therapies
14. Alcohol and street drugs: risks in bipolar illness
12. Psychopharmacology vs alternative therapies
13. Risk associated with treatment withdrawal
12. Psychopharmacology vs alternative therapies
13. Risk associated with treatment withdrawal
15. Early detection of manic and hypomanic episodes
13. Risk associated with treatment withdrawal
14. Alcohol and street drugs: risks in bipolar illness
14. Alcohol and street drugs: risks in bipolar illness
16. Early detection of depressive and mixed episodes
14. Alcohol and street drugs: risks in bipolar illness
15. Early detection of manic and hypomanic episodes
17. What to do when a new phase is detected? sodes
15. Early detection of manic and hypomanic epi
16. Early detection of depressive and mixed episodes
15. Early detection of manic and hypomanic episodes
16. Early detection of depressive and mixed episodes
18. Regularity
16. Early detection of depressive and mixed episodes
17. What to do when a new phase is detected?
19. Stress management techniques
17. What to do when a new phase is detected?
18. Regularity
17. What to do when a new phase is detected?
20. Problem-solving techniques
18. Regularity
18. Regularity agement techniques
19. Stress man
21. Final sessions
19. Stress management techniques
19. Stress management techniques
20. Problem-solving techniques
20. Problem-solving techniques
20. Problem-solving techniques
21. Final sessions
Source: Colom F, Vieta E, Martínez-Arán A, et al. A Randomized Trial on the Efficacy of Group
21. Final sessions
Psychoeducation in the Prophylaxis of Recurrences in Bipolar Patients Whose Disease Is in
21. Final sessions
Source: Colom F, Vieta E, Martínez-Arán A, et al. A Randomized Trial on the Efficacy of Group
Remission. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(4):402–407.
Source: Colom F, Vieta E, Martínez-Arán A, et al. A Randomized Trial on the Efficacy of Group
Psychoeducation in the Prophylaxis of Recurrences in Bipolar Patients Whose Disease Is in
Source: Colom F, Vieta E, Martínez-Arán A, et al. A Randomized Trial on the Efficacy of Group
Psychoeducation in the Prophylaxis of Recurrences in Bipolar Patients Whose Disease Is in
Remission. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(4):402–407.
Psychoeducation in the Prophylaxis of Recurrences in Bipolar Patients Whose Disease Is in
Remission. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(4):402–407.
Remission. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60(4):402–407.
56
56
56
56
56