Page 405 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 405
Thoracic wall and Diaphragm 395
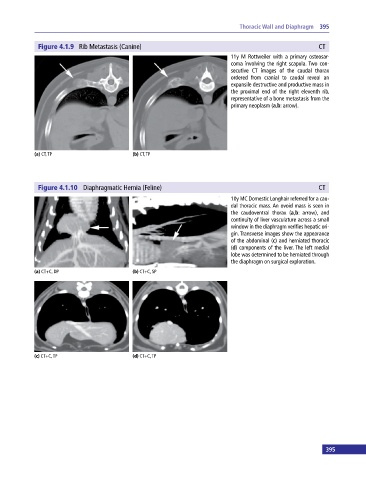
Figure 4.1.9 Rib Metastasis (Canine) CT
11y M Rottweiler with a primary osteosar-
coma involving the right scapula. Two con-
secutive CT images of the caudal thorax
ordered from cranial to caudal reveal an
expansile destructive and productive mass in
the proximal end of the right eleventh rib,
representative of a bone metastasis from the
primary neoplasm (a,b: arrow).
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP
Figure 4.1.10 Diaphragmatic Hernia (Feline) CT
10y MC Domestic Longhair referred for a cau-
dal thoracic mass. An ovoid mass is seen in
the caudoventral thorax (a,b: arrow), and
continuity of liver vasculature across a small
window in the diaphragm verifies hepatic ori-
gin. Transverse images show the appearance
of the abdominal (c) and herniated thoracic
(d) components of the liver. The left medial
lobe was determined to be herniated through
the diaphragm on surgical exploration.
(a) CT+C, DP (b) CT+C, SP
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP
394 395