Page 517 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 517
Hepatovascular Disorders 507
Legend for Figures 5.2.1–5.2.18
A Aorta LP Left portal branch
AZ Azygos vein LG Left gastric artery
C Caudal vena cava LGV Left gastric vein
CD Caudal mesenteric vein P Portal vein
CR Cranial mesenteric vein PH Phrenic vein
GA Gastroduodenal artery RP Right portal branch
GD Gastroduodenal vein RGA Right gastric artery
H Hepatic artery RG Right gastric vein
HB Hepatic artery branch RM Right medial branch hepatic vein
J Jejunal vein RMP Right medial portal branch
L Left hepatic vein S Splenic vein
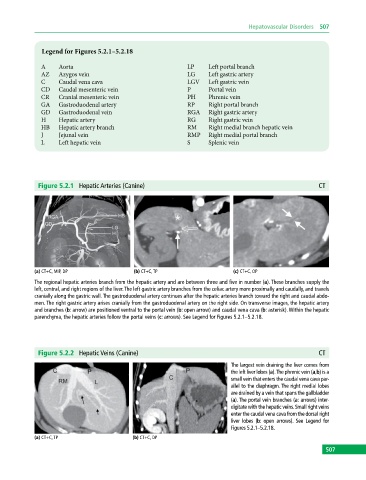
Figure 5.2.1 Hepatic Arteries (Canine) CT
(a) CT+C, MIP, DP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, OP
The regional hepatic arteries branch from the hepatic artery and are between three and five in number (a). These branches supply the
left, central, and right regions of the liver. The left gastric artery branches from the celiac artery more proximally and caudally, and travels
cranially along the gastric wall. The gastroduodenal artery continues after the hepatic arteries branch toward the right and caudal abdo-
men. The right gastric artery arises cranially from the gastroduodenal artery on the right side. On transverse images, the hepatic artery
and branches (b: arrow) are positioned ventral to the portal vein (b: open arrow) and caudal vena cava (b: asterisk). Within the hepatic
parenchyma, the hepatic arteries follow the portal veins (c: arrows). See Legend for Figures 5.2.1–5.2.18.
Figure 5.2.2 Hepatic Veins (Canine) CT
The largest vein draining the liver comes from
the left liver lobes (a). The phrenic vein (a,b) is a
small vein that enters the caudal vena cava par-
allel to the diaphragm. The right medial lobes
are drained by a vein that spans the gallbladder
(a). The portal vein branches (a: arrows) inter-
digitate with the hepatic veins. Small right veins
enter the caudal vena cava from the dorsal right
liver lobes (b: open arrows). See Legend for
Figures 5.2.1–5.2.18.
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, DP
507