Page 28 - ILCC BUSINESS COMPUTER APPS SYLLABUS FALL 2017
P. 28
Screen Components
Each window screen contains similar components, such as a title bar, menu bar, and toolbar. Most
programs contain many commands (actions) that you use to work with the program. Many of these
commands are organized under menus and in dialog boxes. Like a restaurant menu, a program menu
shows you a list of choices. To keep the screen uncluttered, menus are closed until you click their tabs,
located just underneath the title bar. For example, clicking "File" in the Word menu bar displays the
menu choices for handling files.
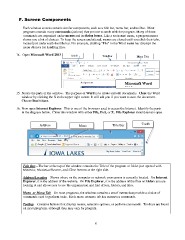
14. Open Microsoft Word 2013 again. Quick Title Bar Menu Tabs
Access
Microsoft Word
2013
15. Notice the parts of the window. The purpose of Word is to create and edit documents. Close the Word
window by clicking the X in the upper right corner. It will ask you if you want to save the document.
Choose Don’t Save.
16. Now open Internet Explorer. This is one of the browsers used to access the Internet. Identify the parts
in the diagram below. Close this window with either File, Exit, or X. File Explorer should remain open.
Address Menu Title Bar Toolb
Bar Bar ars
Title Bar—The bar at the top of the window contains the Title of the program or folder just opened with
Minimize, Maximize/Restore, and Close buttons at the right side.
Address/Location—Shows where on the computer or network your cursor is currently located. On Internet
Explorer, it is the address of the website. On File Explorer, it is the address of the files or folders you are
looking at and allows you to see the organization and find drives, folders, and files.
Menu or Menu Tab—On most programs, the window contains a set of menus that provide a choice of
commands used to perform tasks. Each menu or menu tab has numerous commands.
Toolbar—Contains buttons that display menus, selection options, or perform commands. Toolbars are found
on most programs, although they may vary by program.
8
Each window screen contains similar components, such as a title bar, menu bar, and toolbar. Most
programs contain many commands (actions) that you use to work with the program. Many of these
commands are organized under menus and in dialog boxes. Like a restaurant menu, a program menu
shows you a list of choices. To keep the screen uncluttered, menus are closed until you click their tabs,
located just underneath the title bar. For example, clicking "File" in the Word menu bar displays the
menu choices for handling files.
14. Open Microsoft Word 2013 again. Quick Title Bar Menu Tabs
Access
Microsoft Word
2013
15. Notice the parts of the window. The purpose of Word is to create and edit documents. Close the Word
window by clicking the X in the upper right corner. It will ask you if you want to save the document.
Choose Don’t Save.
16. Now open Internet Explorer. This is one of the browsers used to access the Internet. Identify the parts
in the diagram below. Close this window with either File, Exit, or X. File Explorer should remain open.
Address Menu Title Bar Toolb
Bar Bar ars
Title Bar—The bar at the top of the window contains the Title of the program or folder just opened with
Minimize, Maximize/Restore, and Close buttons at the right side.
Address/Location—Shows where on the computer or network your cursor is currently located. On Internet
Explorer, it is the address of the website. On File Explorer, it is the address of the files or folders you are
looking at and allows you to see the organization and find drives, folders, and files.
Menu or Menu Tab—On most programs, the window contains a set of menus that provide a choice of
commands used to perform tasks. Each menu or menu tab has numerous commands.
Toolbar—Contains buttons that display menus, selection options, or perform commands. Toolbars are found
on most programs, although they may vary by program.
8