Page 209 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 209
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
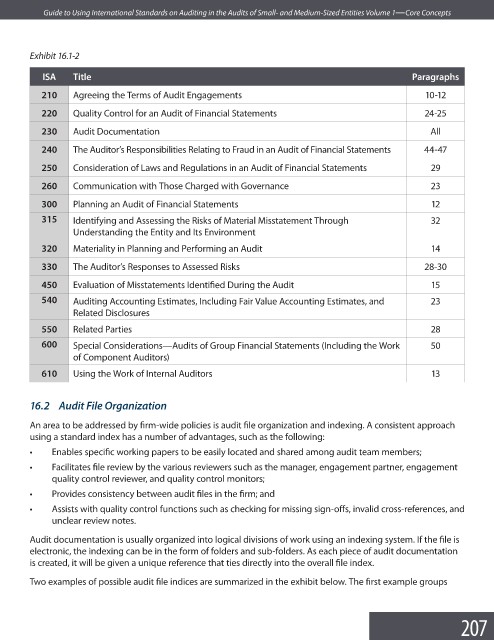
Exhibit 16.1-2
ISA Title Paragraphs
210 Agreeing the Terms of Audit Engagements 10-12
220 Quality Control for an Audit of Financial Statements 24-25
230 Audit Documentation All
240 The Auditor’s Responsibilities Relating to Fraud in an Audit of Financial Statements 44-47
250 Consideration of Laws and Regulations in an Audit of Financial Statements 29
260 Communication with Those Charged with Governance 23
300 Planning an Audit of Financial Statements 12
315 Identifying and Assessing the Risks of Material Misstatement Through 32
Understanding the Entity and Its Environment
320 Materiality in Planning and Performing an Audit 14
330 The Auditor’s Responses to Assessed Risks 28-30
450 Evaluation of Misstatements Identified During the Audit 15
540 Auditing Accounting Estimates, Including Fair Value Accounting Estimates, and 23
Related Disclosures
550 Related Parties 28
600 Special Considerations—Audits of Group Financial Statements (Including the Work 50
of Component Auditors)
610 Using the Work of Internal Auditors 13
16.2 Audit File Organization
An area to be addressed by firm-wide policies is audit file organization and indexing. A consistent approach
using a standard index has a number of advantages, such as the following:
• Enables specific working papers to be easily located and shared among audit team members;
• Facilitates file review by the various reviewers such as the manager, engagement partner, engagement
quality control reviewer, and quality control monitors;
• Provides consistency between audit files in the fi rm; and
• Assists with quality control functions such as checking for missing sign-offs, invalid cross-references, and
unclear review notes.
Audit documentation is usually organized into logical divisions of work using an indexing system. If the fi le is
electronic, the indexing can be in the form of folders and sub-folders. As each piece of audit documentation
is created, it will be given a unique reference that ties directly into the overall fi le index.
Two examples of possible audit file indices are summarized in the exhibit below. The first example groups
207