Page 71 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 71
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
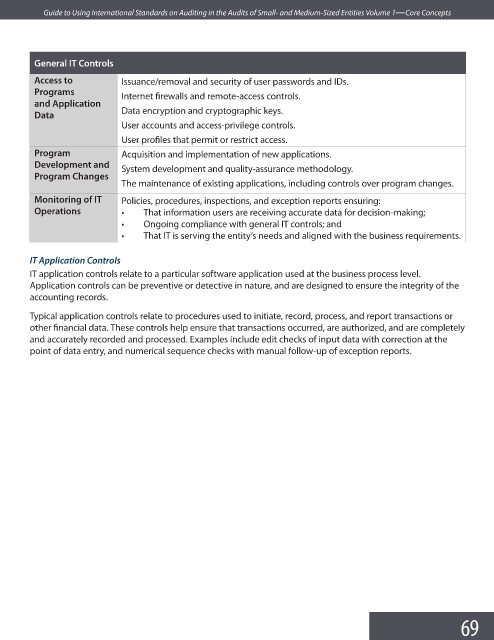
General IT Controls
Access to Issuance/removal and security of user passwords and IDs.
Programs Internet firewalls and remote-access controls.
and Application
Data encryption and cryptographic keys.
Data
User accounts and access-privilege controls.
User profiles that permit or restrict access.
Program Acquisition and implementation of new applications.
Development and System development and quality-assurance methodology.
Program Changes
The maintenance of existing applications, including controls over program changes.
Monitoring of IT Policies, procedures, inspections, and exception reports ensuring:
Operations • That information users are receiving accurate data for decision-making;
• Ongoing compliance with general IT controls; and
• That IT is serving the entity’s needs and aligned with the business requirements.
IT Application Controls
IT application controls relate to a particular software application used at the business process level.
Application controls can be preventive or detective in nature, and are designed to ensure the integrity of the
accounting records.
Typical application controls relate to procedures used to initiate, record, process, and report transactions or
other financial data. These controls help ensure that transactions occurred, are authorized, and are completely
and accurately recorded and processed. Examples include edit checks of input data with correction at the
point of data entry, and numerical sequence checks with manual follow-up of exception reports.
69