Page 74 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 74
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
5.10 Manual versus Automated Controls
For most entities, the system of internal control will consist of a mixture of manual and automated controls.
The risks and benefits associated with the different types of control are outlined below.
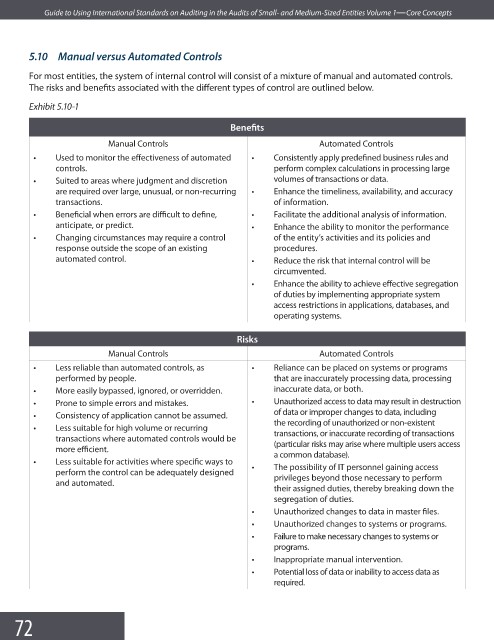
Exhibit 5.10-1
Benefi ts
Manual Controls Automated Controls
• Used to monitor the effectiveness of automated • Consistently apply predefined business rules and
controls. perform complex calculations in processing large
• Suited to areas where judgment and discretion volumes of transactions or data.
are required over large, unusual, or non-recurring • Enhance the timeliness, availability, and accuracy
transactions. of information.
• Beneficial when errors are diffi cult to defi ne, • Facilitate the additional analysis of information.
anticipate, or predict. • Enhance the ability to monitor the performance
• Changing circumstances may require a control of the entity’s activities and its policies and
response outside the scope of an existing procedures.
automated control. • Reduce the risk that internal control will be
circumvented.
• Enhance the ability to achieve eff ective segregation
of duties by implementing appropriate system
access restrictions in applications, databases, and
operating systems.
Risks
Manual Controls Automated Controls
• Less reliable than automated controls, as • Reliance can be placed on systems or programs
performed by people. that are inaccurately processing data, processing
• More easily bypassed, ignored, or overridden. inaccurate data, or both.
• Prone to simple errors and mistakes. • Unauthorized access to data may result in destruction
of data or improper changes to data, including
• Consistency of application cannot be assumed.
the recording of unauthorized or non-existent
• Less suitable for high volume or recurring
transactions where automated controls would be transactions, or inaccurate recording of transactions
(particular risks may arise where multiple users access
more effi cient.
a common database).
• Less suitable for activities where specific ways to
perform the control can be adequately designed • The possibility of IT personnel gaining access
and automated. privileges beyond those necessary to perform
their assigned duties, thereby breaking down the
segregation of duties.
• Unauthorized changes to data in master fi les.
• Unauthorized changes to systems or programs.
• Failure to make necessary changes to systems or
programs.
• Inappropriate manual intervention.
• Potential loss of data or inability to access data as
required.
72