Page 425 - TaxAdviser_2022
P. 425
CAMPUS TO CLIENTS
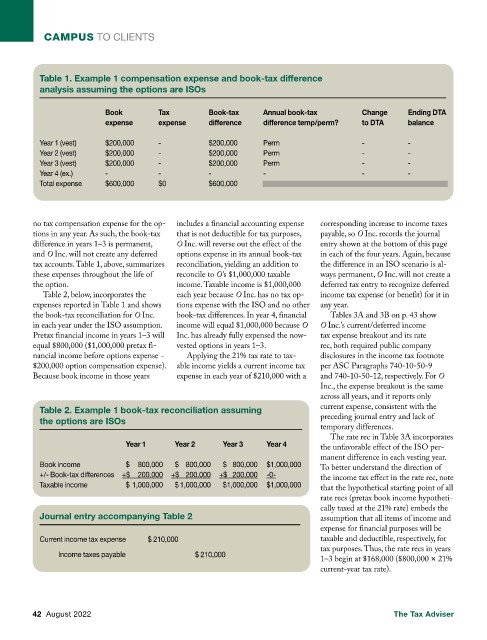
Table 1. Example 1 compensation expense and book-tax difference
analysis assuming the options are ISOs
Book Tax Book-tax Annual book-tax Change Ending DTA
expense expense difference difference temp/perm? to DTA balance
Year 1 (vest) $200,000 - $200,000 Perm - -
Year 2 (vest) $200,000 - $200,000 Perm - -
Year 3 (vest) $200,000 - $200,000 Perm - -
Year 4 (ex.) - - - - - -
Total expense $600,000 $0 $600,000
no tax compensation expense for the op- includes a financial accounting expense corresponding increase to income taxes
tions in any year. As such, the book-tax that is not deductible for tax purposes, payable, so O Inc. records the journal
difference in years 1–3 is permanent, O Inc. will reverse out the effect of the entry shown at the bottom of this page
and O Inc. will not create any deferred options expense in its annual book-tax in each of the four years. Again, because
tax accounts. Table 1, above, summarizes reconciliation, yielding an addition to the difference in an ISO scenario is al-
these expenses throughout the life of reconcile to O’s $1,000,000 taxable ways permanent, O Inc. will not create a
the option. income. Taxable income is $1,000,000 deferred tax entry to recognize deferred
Table 2, below, incorporates the each year because O Inc. has no tax op- income tax expense (or benefit) for it in
expenses reported in Table 1 and shows tions expense with the ISO and no other any year.
the book-tax reconciliation for O Inc. book-tax differences. In year 4, financial Tables 3A and 3B on p. 43 show
in each year under the ISO assumption. income will equal $1,000,000 because O O Inc.’s current/deferred income
Pretax financial income in years 1–3 will Inc. has already fully expensed the now- tax expense breakout and its rate
equal $800,000 ($1,000,000 pretax fi- vested options in years 1–3. rec, both required public company
nancial income before options expense − Applying the 21% tax rate to tax- disclosures in the income tax footnote
$200,000 option compensation expense). able income yields a current income tax per ASC Paragraphs 740-10-50-9
Because book income in those years expense in each year of $210,000 with a and 740-10-50-12, respectively. For O
Inc., the expense breakout is the same
across all years, and it reports only
Table 2. Example 1 book-tax reconciliation assuming current expense, consistent with the
the options are ISOs preceding journal entry and lack of
temporary differences.
The rate rec in Table 3A incorporates
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 the unfavorable effect of the ISO per-
manent difference in each vesting year.
Book income $ 800,000 $ 800,000 $ 800,000 $1,000,000 To better understand the direction of
+/- Book-tax differences +$ 200,000 +$ 200,000 +$ 200,000 -0- the income tax effect in the rate rec, note
Taxable income $ 1,000,000 $ 1,000,000 $ 1,000,000 $1,000,000 that the hypothetical starting point of all
rate recs (pretax book income hypotheti-
cally taxed at the 21% rate) embeds the
Journal entry accompanying Table 2 assumption that all items of income and
expense for financial purposes will be
Current income tax expense $ 210,000 taxable and deductible, respectively, for
tax purposes. Thus, the rate recs in years
Income taxes payable $ 210,000
1–3 begin at $168,000 ($800,000 × 21%
current-year tax rate).
42 August 2022 The Tax Adviser