Page 429 - TaxAdviser_2022
P. 429
CAMPUS TO CLIENTS
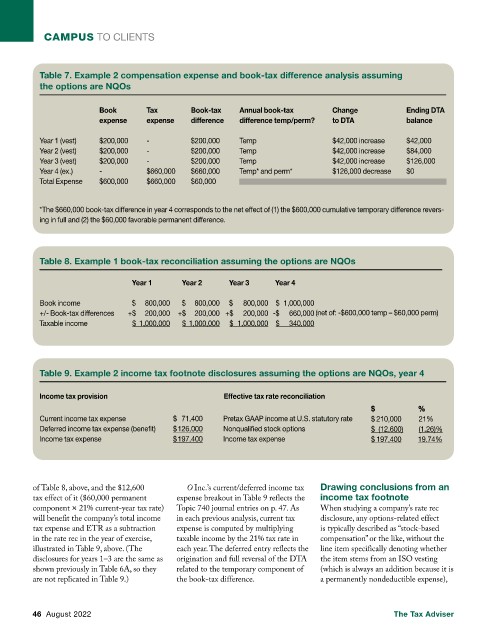
Table 7. Example 2 compensation expense and book-tax difference analysis assuming
the options are NQOs
Book Tax Book-tax Annual book-tax Change Ending DTA
expense expense difference difference temp/perm? to DTA balance
Year 1 (vest) $200,000 - $200,000 Temp $42,000 increase $42,000
Year 2 (vest) $200,000 - $200,000 Temp $42,000 increase $84,000
Year 3 (vest) $200,000 - $200,000 Temp $42,000 increase $126,000
Year 4 (ex.) - $660,000 $660,000 Temp* and perm* $126,000 decrease $0
Total Expense $600,000 $660,000 $60,000
*The $660,000 book-tax difference in year 4 corresponds to the net effect of (1) the $600,000 cumulative temporary difference revers-
ing in full and (2) the $60,000 favorable permanent difference.
Table 8. Example 1 book-tax reconciliation assuming the options are NQOs
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4
Book income $ 800,000 $ 800,000 $ 800,000 $ 1,000,000
+/- Book-tax differences +$ 200,000 +$ 200,000 +$ 200,000 -$ 660,000 (net of: -$600,000 temp – $60,000 perm)
Taxable income $ 1,000,000 $ 1,000,000 $ 1,000,000 $ 340,000
Table 9. Example 2 income tax footnote disclosures assuming the options are NQOs, year 4
Income tax provision Effective tax rate reconciliation
$ % %
Current income tax expense $ 71,400 Pretax GAAP income at U.S. statutory rate $ 210,000 21%
Deferred income tax expense (benefit) $ 126,000 Nonqualified stock options $ (12,600) (1.26)%
Income tax expense $ 197,400 Income tax expense $ 197,400 19.74%
of Table 8, above, and the $12,600 O Inc.’s current/deferred income tax Drawing conclusions from an
tax effect of it ($60,000 permanent expense breakout in Table 9 reflects the income tax footnote
component × 21% current-year tax rate) Topic 740 journal entries on p. 47. As When studying a company’s rate rec
will benefit the company’s total income in each previous analysis, current tax disclosure, any options-related effect
tax expense and ETR as a subtraction expense is computed by multiplying is typically described as “stock-based
in the rate rec in the year of exercise, taxable income by the 21% tax rate in compensation” or the like, without the
illustrated in Table 9, above. (The each year. The deferred entry reflects the line item specifically denoting whether
disclosures for years 1–3 are the same as origination and full reversal of the DTA the item stems from an ISO vesting
shown previously in Table 6A, so they related to the temporary component of (which is always an addition because it is
are not replicated in Table 9.) the book-tax difference. a permanently nondeductible expense),
46 August 2022 The Tax Adviser