Page 427 - TaxAdviser_2022
P. 427
CAMPUS TO CLIENTS
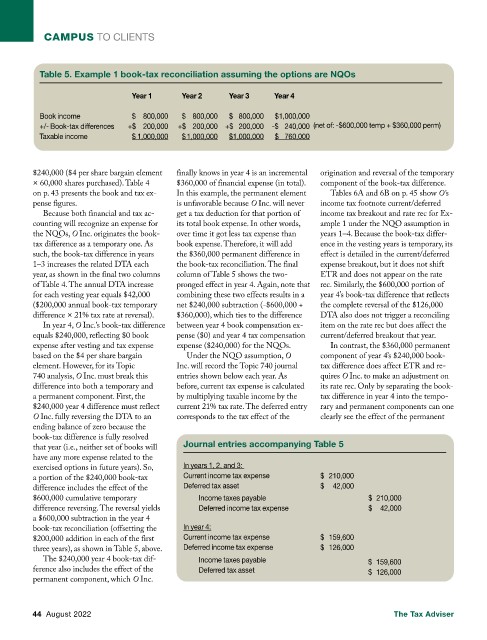
Table 5. Example 1 book-tax reconciliation assuming the options are NQOs
Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4
Book income $ 800,000 $ 800,000 $ 800,000 $ 1,000,000
+/- Book-tax differences +$ 200,000 +$ 200,000 +$ 200,000 -$ 240,000 (net of: -$600,000 temp + $360,000 perm)
Taxable income $ 1,000,000 $ 1,000,000 $ 1,000,000 $ 760,000
$240,000 ($4 per share bargain element finally knows in year 4 is an incremental origination and reversal of the temporary
× 60,000 shares purchased). Table 4 $360,000 of financial expense (in total). component of the book-tax difference.
on p. 43 presents the book and tax ex- In this example, the permanent element Tables 6A and 6B on p. 45 show O’s
pense figures. is unfavorable because O Inc. will never income tax footnote current/deferred
Because both financial and tax ac- get a tax deduction for that portion of income tax breakout and rate rec for Ex-
counting will recognize an expense for its total book expense. In other words, ample 1 under the NQO assumption in
the NQOs, O Inc. originates the book- over time it got less tax expense than years 1–4. Because the book-tax differ-
tax difference as a temporary one. As book expense. Therefore, it will add ence in the vesting years is temporary, its
such, the book-tax difference in years the $360,000 permanent difference in effect is detailed in the current/deferred
1–3 increases the related DTA each the book-tax reconciliation. The final expense breakout, but it does not shift
year, as shown in the final two columns column of Table 5 shows the two- ETR and does not appear on the rate
of Table 4. The annual DTA increase pronged effect in year 4. Again, note that rec. Similarly, the $600,000 portion of
for each vesting year equals $42,000 combining these two effects results in a year 4’s book-tax difference that reflects
($200,000 annual book-tax temporary net $240,000 subtraction (-$600,000 + the complete reversal of the $126,000
difference × 21% tax rate at reversal). $360,000), which ties to the difference DTA also does not trigger a reconciling
In year 4, O Inc.’s book-tax difference between year 4 book compensation ex- item on the rate rec but does affect the
equals $240,000, reflecting $0 book pense ($0) and year 4 tax compensation current/deferred breakout that year.
expense after vesting and tax expense expense ($240,000) for the NQOs. In contrast, the $360,000 permanent
based on the $4 per share bargain Under the NQO assumption, O component of year 4’s $240,000 book-
element. However, for its Topic Inc. will record the Topic 740 journal tax difference does affect ETR and re-
740 analysis, O Inc. must break this entries shown below each year. As quires O Inc. to make an adjustment on
difference into both a temporary and before, current tax expense is calculated its rate rec. Only by separating the book-
a permanent component. First, the by multiplying taxable income by the tax difference in year 4 into the tempo-
$240,000 year 4 difference must reflect current 21% tax rate. The deferred entry rary and permanent components can one
O Inc. fully reversing the DTA to an corresponds to the tax effect of the clearly see the effect of the permanent
ending balance of zero because the
book-tax difference is fully resolved
that year (i.e., neither set of books will Journal entries accompanying Table 5
have any more expense related to the
In years 1, 2, and 3:
exercised options in future years). So,
Current income tax expense $ 210,000
a portion of the $240,000 book-tax
Deferred tax asset $ 42,000
difference includes the effect of the
$600,000 cumulative temporary Income taxes payable $ 210,000
difference reversing. The reversal yields Deferred income tax expense $ 42,000
a $600,000 subtraction in the year 4
book-tax reconciliation (offsetting the In year 4:
$200,000 addition in each of the first Current income tax expense $ 159,600
three years), as shown in Table 5, above. Deferred income tax expense $ 126,000
The $240,000 year 4 book-tax dif- Income taxes payable $ 159,600
ference also includes the effect of the Deferred tax asset $ 126,000
permanent component, which O Inc.
44 August 2022 The Tax Adviser