Page 169 - Clinical Manual of Small Animal Endosurgery
P. 169
Operative Laparoscopy 157
(a)
(b)
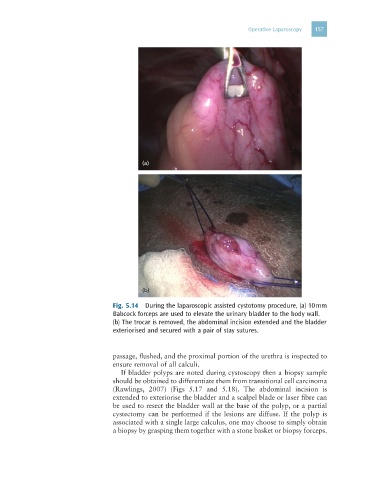
Fig. 5.14 During the laparoscopic assisted cystotomy procedure, (a) 10 mm
Babcock forceps are used to elevate the urinary bladder to the body wall.
(b) The trocar is removed, the abdominal incision extended and the bladder
exteriorised and secured with a pair of stay sutures.
passage, flushed, and the proximal portion of the urethra is inspected to
ensure removal of all calculi.
If bladder polyps are noted during cystoscopy then a biopsy sample
should be obtained to differentiate them from transitional cell carcinoma
(Rawlings, 2007) (Figs 5.17 and 5.18). The abdominal incision is
extended to exteriorise the bladder and a scalpel blade or laser fibre can
be used to resect the bladder wall at the base of the polyp, or a partial
cystectomy can be performed if the lesions are diffuse. If the polyp is
associated with a single large calculus, one may choose to simply obtain
a biopsy by grasping them together with a stone basket or biopsy forceps.